Why was Pluto kicked out of the nine planets?
Have you ever asked yourself why Pluto was expelled from nine planets? Why did astronomers decide to snatch this small planet from the list of solar planets? This question intrigues many people, and prompts us to discover behind the scenes to find out the truth about it.
Show key points
- Pluto was reclassified from a planet to a dwarf planet in 2006 due to its failure to meet the new criteria defined by the International Astronomical Union.
- Despite being considered the ninth planet since its discovery in 1930, Pluto's small size and dim visibility raised doubts about its planetary status.
- Its unusual characteristics, such as an eccentric orbit and icy composition, set it apart from other major planets and contributed to debates around its classification.
- ADVERTISEMENT
- The definition of a planet now requires an object to orbit the Sun, be spherical, and have cleared its orbit of other debris—criteria Pluto does not fully satisfy.
- Pluto remains scientifically significant and continues to intrigue researchers with its unique features and potential secrets.
- Future space missions may provide deeper insights into Pluto's atmosphere and geology, possibly reshaping our understanding of this distant body.
- Beyond scientific interest, Pluto could also serve as a site for research, exploration, or even space tourism in the future due to its captivating and mysterious nature.
1. Pluto: The lost planet in the solar system.
As the smallest planet and farthest from the sun, Pluto is one of the most unusual celestial bodies in the solar system. Since its discovery in 1930 by American astronomer Clyde Tomboh, Pluto has been on the list of solar planets for more than six decades. However, Pluto has become the subject of considerable controversy in recent decades, eventually leading to his expulsion from the list of major planets.
Recommend
Pluto has always been particularly famous, as it was considered the only buffer planet in the solar system. But what made it different was its very small size compared to other planets. While the diameter of the Earth is about 12,742 kilometers, Pluto is only 2,372 kilometers in diameter, much less than the size of the Moon. Therefore, some have been questioning Pluto's suitability to be a planet.
But despite its small size, Pluto retains a distinguished history in the scientific community. When discovered, it was considered the farthest known celestial body in the solar system. No other planet in the solar system was discovered after Pluto for 76 years, until Eris was discovered in 2005. However, more discoveries began in a group of small objects after that, raising questions about what Pluto is and if it should be part of the planets.
Contrary to what is known, the decision to expel Pluto was based on an official definition of planets adopted in 2006 by the International Astronomical Union. According to this definition, a planet must meet three criteria: it must have a spherical shape, be surrounded by a thin layer of gas or liquid, and must clean the surrounding area from other celestial bodies. Given these criteria, it has become clear that Pluto does not meet the requirements necessary for the planet.
However, the expulsion of Pluto from the list of planets does not mean the end of his story. In addition to its own position in the solar system, Pluto has a scientific and aesthetic significance that cannot be ignored. Even if it is not considered a major planet, it still holds a lot of mystery and magic. The future may open new doors to our understanding of the planet, as it could contain answers that change our outlook forever.
2. First notes: discover the size of Pluto's small size.

When Pluto was first discovered in 1930, initial observations were pointing to its small size compared to other planets in the solar system. At the time, Pluto was thought to be the largest object in the far Kuiper belt after Neptune. However, its small size and poor brightness were mysterious to astronomers.
But with the development of technology and advances in observatories and telescopes, accurate information began to emerge about the size of Pluto. It turns out to be a small planet with a diameter of only about 2370 kilometers, which means that it is much smaller than other planets in the solar system such as Earth, Mars and even Ether.
The discovery has raised big questions among scientists, as planets are usually huge and clearly visible beings. Although Pluto was considered huge in the far Kuiper belt, comparing it to other planets made it look small.
However, Pluto's size wasn't the only stop to the exotic, its poor brightness was also puzzling to scientists. Pluto was hard to see even with powerful telescopes, and this made it look like a dark and frowning planet in the sky.
The discovery of Pluto's small size and weak brightness were the beginning of a mysterious and exciting journey to discover why it was expelled from nine planets, and a prelude to radical changes in its classification as a planet.
3. Reservations of astronomers: the incompatibility of some characteristics with the definition of the planet.
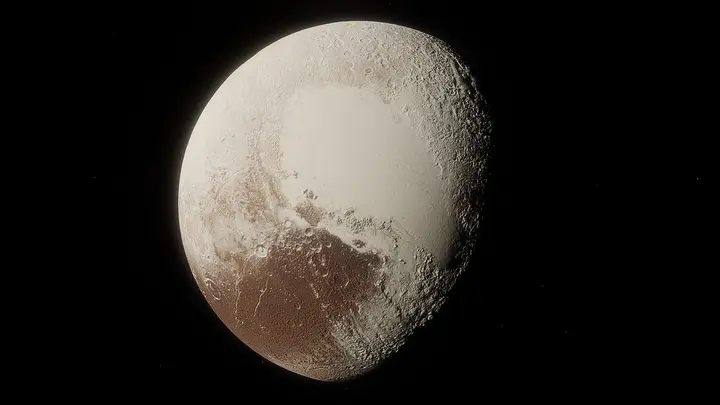

When discussions about placing Pluto on the planetary list began many years ago, it had a number of properties that did not correspond to the definition of planets adopted at the time. Astronomers were having difficulty including them in the same distinct category as other planets such as Earth, Mars and Saturn.
One of the main reservations was Pluto's very small size compared to other planets. It was very small in diameter, and therefore did not meet the standard required to be considered a planet by the definition at the time.
In addition, there are reservations about the quality of Pluto's constituent material and its geological composition. Unlike other planets that are mostly composed of rocks and minerals, Pluto's surface is made up of a mixture of ice and icy rock. These different properties gave Pluto a unique identity, but made it different from other planets in the definitions of astronomy.
Moreover, there have been reservations about Pluto's orbit and its relationship to the constellation of other planets. Pluto has a highly ecritable and unstable orbit, sometimes passing closer than Neptune in the solar system. This irregular movement was contrary to the main characteristic of the planets, which is their regular motion and maintaining their orbits around the sun.
Thus, astronomers' reservations lay in the incompatibility of some of Pluto's unique properties with the official definition of planets of the period. It was recognized that despite its importance and scientific value, Pluto belonged to a different class from the classical planets of the solar system. This prompted scientists to rethink definitions and classifications and declare Pluto as another astronomical object rather than a planet.
4. A new definition of planets: the active role of the International Astronomical Union.
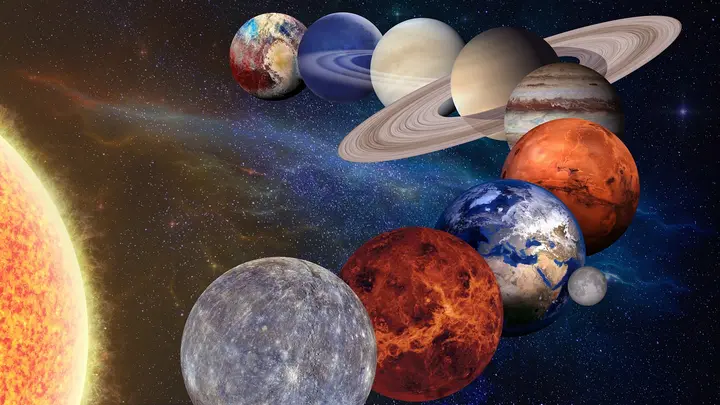

When it comes to defining planets, it's not easy and obvious. Planets are massive bodies orbiting the sun, but how do we determine which object really deserves to be a "planet"? This is the question that necessitated the intervention of the International Astronomical Union.
In 2006, the International Astronomical Union announced a new definition of planets. Until then, there were nine recognized planets in our solar system, including Pluto. But the International Astronomical Union considered it necessary to define new criteria for planetary classification.
According to the new definition, planets must meet three basic conditions. First, the constellation must orbit the Sun or another star; second, it must have enough mass to achieve spherical balance, which means it is almost spherical in shape; and finally, it must have displaced other material from its own path.
Based on these criteria, the International Astronomical Union found that Pluto did not meet the new criteria for planetary classification. Pluto does not have enough mass to be almost spherical and has not actually displaced other material from its path. So, it was then declared a "dwarf planet" rather than a "planet."
The decision of the International Astronomical Union was not without controversy. The incident of Pluto's ejection from nine planets sparked many debates and debates among scientists and amateurs alike. There are those who see it as a rational decision, as the definition of the planet must be specific and precise. There are those who consider this an unfair decision, as they believe that Pluto deserves to be part of the solar planets.
However, this new definition of planets was not the end of Pluto's journey. The small planet continues to attract attention, and there are many space missions aimed at better studying Pluto and understanding it more deeply. Perhaps in the future, new standards will emerge that will make us look at Pluto differently and eventually recognize it as a real planet.
5. Pluto's future: what does it hold for this excluded planet?

Pluto's fate still seems to be a mystery and puzzling, so what awaits this small planet after being expelled from nine planets? Will it remain just an excluded astronomical body or does it have a bright future ahead of it? Let's explore together some possible scenarios for Pluto's uncertain future.
The future could see Pluto return strongly to the spotlight and regain its status as an important part of the solar system. Some future studies and research may have exciting insights that may make us narrate Pluto with new eyes. It may have a special configuration that differs from other planets, providing an opportunity to study its atmospheric system and internal structure in detail. Pluto may be a small planet, but it holds a big secret waiting to be revealed.
It is also possible that Pluto's future is linked to the trends of space exploration, as humans move towards exploring celestial bodies and colonizing planets, Pluto may have an important role to play in this context. It may become a space station for short space flights or a center for astronomical and geological research to explore its mysterious depths. Pluto may be the first interface for humans on their journey towards the stars.
Pluto is likely to find a special destiny as a unique tourist destination. It can be exciting and adventurous to travel to this excluded planet, discover its icy terrain and experience strange weather currents. Visitors may wait to watch the stunning sunrise on Pluto's deck or wander among its majestic mountains. Pluto's unique character makes it an unconventional tourist destination that will undoubtedly be attractive to many explorers and adventurers.
In terms of technology, a space mission may be developed to explore Pluto more deeply. We could see a spacecraft carrying scientists and astronauts towards this distant planet to collect more data and information about it. This mission may open new doors to the exploration of minor planets and expand our knowledge of the entire solar system.
In conclusion, the future of Pluto is still unknown, but this small planet certainly holds a lot of secrets and possibilities. He may one day return to regain his place among the planets or become a tourist destination or an astronomical research center. It's an unpredictable future, and that's where the magic of this unlikely planet lies.

After this exciting journey into the world of Pluto, we discover that the decision to expel Pluto from nine planets was based on precise scientific rules and a specific definition of planets. Pluto may be smaller than this noble list, but he still holds a lot of mysteries and wonders in his small world. Perhaps in the future, we will see new developments that make us see Pluto from a completely different perspective. The planet has a scientific and aesthetic appeal that cannot be ignored, even if it is not part of nine planets.
![]()
The most important technical programs for mobile and computer that are indispensable for everyone
Mobile phones and computers are essential in modern life, and with the right free tools, they can boost your productivity and simplify daily tasks. Apps like Google Chrome, Google Drive, LibreOffice, and VLC Media Player are easy to use and help you stay efficient, secure, and entertained. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
Clothing Trading - Hidden Tetanus Discovery
Clothing trade can be highly profitable when you understand fashion trends, know your target customers, and offer quality products at affordable prices. Choosing the right type—like children’s or women’s wear—and selecting a smart location or online platform can boost success. Marketing and customer service also play big roles. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
Will the earth keep heating up?
The summer of 2023 brought record heat, fierce wildfires, and deadly monsoons—clear signs of worsening climate change. Scientists warn we’re edging close to the 1.5°C global warming limit, urging urgent action. Real change means cutting emissions now and rethinking our everyday choices—are we ready to act? more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
9 reasons why small businesses fail
9 reasons why small businesses fail more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
AI inspires creativity: artists and musicians use AI for their creations
AI is reshaping creativity, helping artists and musicians explore new styles and techniques. Tools like Soundraw let anyone compose music quickly, while artists like Ruby Barat use AI to transform classic art. Though some fear it may dilute originality, AI is opening bold new paths in creative expression. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
Motivation: How to Start and Stay Motivated
Motivation: How to get started and staying motivated more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
Valuable life skills gained from mountaineering
Mountaineering is more than climbing; it’s a journey that builds resilience, self-reliance, and teamwork. It teaches us to accept failure, embrace challenges, and grow through every step. The real reward isn’t reaching the summit, but gaining the strength and wisdom needed to navigate life itself. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
Explore the magic of Belfast: from ship history to contemporary art culture
Belfast blends rich shipbuilding history with vibrant culture, stunning modern architecture, and lively arts. From Titanic’s legacy to music festivals and scenic parks, the city offers unforgettable experiences. Stroll markets, enjoy local dishes, and soak in the warmth of a place where tradition meets creativity. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
75% of the global diet is produced by just 12 plants and 5 different animals
75% of the global diet is produced by just 12 plants and 5 different animals more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
Does pregnancy accelerate "biological aging"?
A study in the Philippines found that pregnancy may speed up biological aging in women, with each pregnancy linked to about 4 to 4.5 months of aging. This effect wasn't seen in men, and varied depending on context. Researchers hope these insights might guide future anti-aging treatments. more- ADVERTISEMENT





















