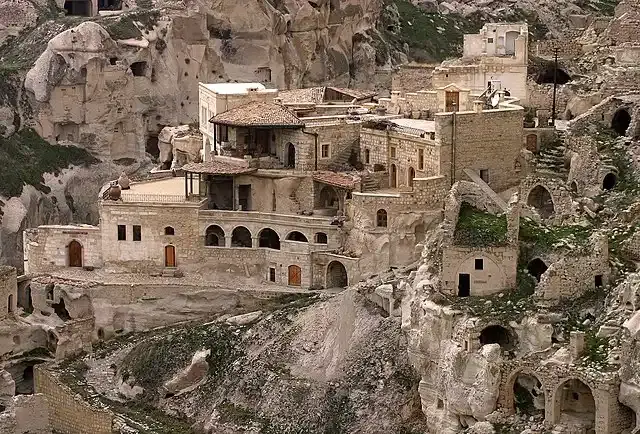
Cappadocia... The ancient city of caves and mountain chimneys in Turkey
In the east of the Anatolian Plateau in present-day central Turkey, specifically in the Nevsehir region, the historical region of Cappadocia is located on the rugged plateau north of the Taurus Mountains. The boundaries of Cappadocia changed through the ages, but retained picturesque landscapes and large expanses of soft volcanic rocks, towers, valleys and caves. Carved rock-cut churches with numerous underground tunnels from the Byzantine and Islamic eras are scattered throughout rural Cappadocia, giving it a special distinction as a tourist destination rarely found in the world, especially the natural mountain chimneys that have been teeming with the region since ancient times.
Show key points
- Cappadocia is a historic region in central Turkey known for its unique geological formations, including soft volcanic rocks, valleys, and fairy chimney rock towers.
- The area has been inhabited since the Neolithic period, as evidenced by ancient pottery, tools, and the remains of the Assyrian-Hittite city of Kanesh discovered in Kultepe.
- The name Cappadocia first appeared in the sixth century BC during Persian rule, a period marked by the spread of Zoroastrianism and continued influence of Persian customs.
- ADVERTISEMENT
- After being overtaken by Alexander the Great and later falling under Seleucid control, Cappadocia eventually aligned with Rome and remained a province until formally annexed by Emperor Tiberius in 17 AD.
- The region experienced repeated conflicts and transitions, including periods of Sassanid destruction and Arab-Muslim occupation, during which extensive cave complexes and shelters were developed.
- Under Seljuk rule following the Byzantine defeat at the Battle of Manzikert in 1071, Cappadocia saw a cultural flourish, with richly decorated rock-cut churches and monasteries being added.
- Today, Cappadocia is a renowned tourist destination famous for its UNESCO-listed sites, such as Goreme National Park, and its unique cave-style accommodations that blend modern hospitality with historical design.
The oldest human monuments in Cappadocia
Recommend

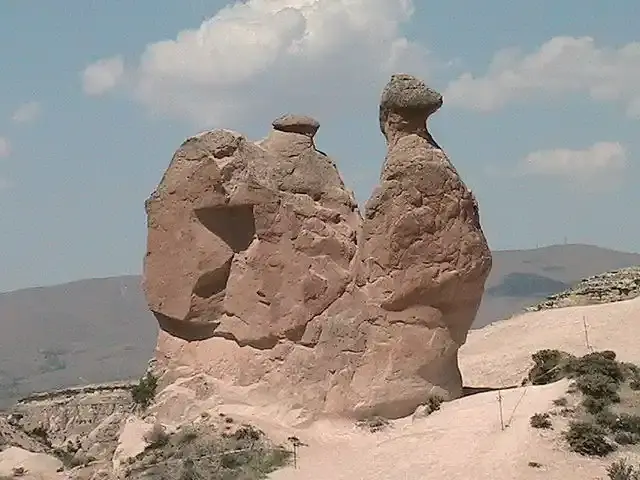
Neolithic pottery and tools found in Cappadocia testify to an early human presence in the area. Excavations in the modern town of Kultepi have uncovered the remains of the Assyrian Hittite city of Kanesh, dating back to the third millennium BC. Tens of thousands of clay tablets found from the remains of an Assyrian trading colony in Kanesh are among the earliest written documents discovered in Turkey.
The first appearance of the name Cappadocia in history
The earliest appearance of the name Cappadocia dates back to the sixth century BC, when the Persians dominated the nobility of Cappadocia and spread Zoroastrianism in the region, where Zoroastrian temple priests were widespread. Due to Cappadocia's rugged terrain and modest agricultural production, the region remained little changed in ancient times, with few important cities built.
Cappadocia between the Persians - Macedonians and Romans

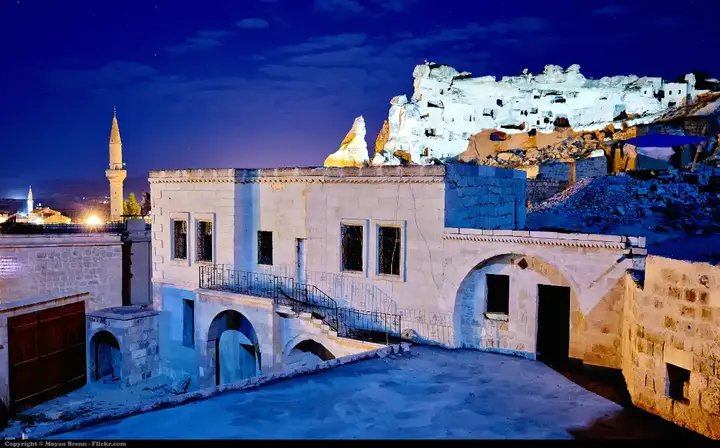
Alexander the Great overtook Cappadocia but sent troops under his general Perdiccas (322 BC). After a power struggle after Alexander's death, Cappadocia fell into the dynastic orbit of the Seleucids, although the local aristocracy descended from the Persian rule period continued to rule and Persian religious practices continued. Cappadocia transferred its allegiance to Rome after the Roman victory at Magnesia (190 BC) and remained faithful despite Pontian and Armenian attacks in the first century BC. Cappadocia was retained as a province of the Roman state until it was annexed by Emperor Tiberius in 17 AD to lead it on the strategic passes of the Taurus Mountains.
Arab rule of Cappadocia

In 611, the Sassanid army destroyed the Cappadocian capital of Caesarea (modern Kayseri), and a few years later the Arab-Muslim conquests began in Cappadocia and lasted until the tenth century. During that period Cappadocia's large complexes of man-made caves and tunnels were built or expanded from existing structures to be used as shelters. However, it has proved difficult to determine specific dates for their construction.
Seljuk rule of the Cappadoca region
Cappadocia enjoyed a period of prosperity in the tenth and eleventh centuries under Islamic rule and some rock-cut churches and monasteries were added. Many surviving churches from this period are richly decorated. The Byzantine Empire permanently lost Cappadocia when it came under the control of the Seljuk Turks as they defeated the Byzantine army at the Battle of Manzikert in 1071, marking the end of Byzantine rule over Cappadocia.
Tourist fame of the Cappadocia region
The name Cappadocia is now widely known in the tourism industry to refer to the area that stretches roughly from Kayseri in the west to Aksaray where there are the largest number of monuments. The most visited attractions include the sprawling underground tunnels of Derinkuyu, Kaymakli and Goreme National Park, where there are a large number of churches and rock-cut dwellings. In 1985, Goreme National Park and other rock sites in the region were classified as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, which increased its fame and the demand of tourists from everywhere, and there were famous hotels designed in the form of caves or rooms carved into rocks similar to the famous design of the Cappadocia area, which made these modern buildings perfectly consistent with the heritage of the region.
![]()
Tranquility and Beauty in Djerba Island in Tunisia
Djerba, or the "Island of Dreams," enchants with its pristine beaches and rich history. Combining the charm of the Mediterranean, its multicultural heritage, and the spirit of local life, it is an ideal destination for relaxation and adventure amidst breathtaking natural landscapes and authentic cultural experiences. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
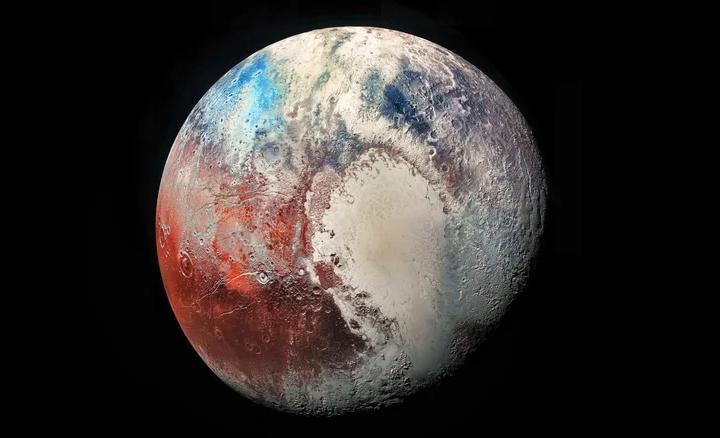
Why was Pluto kicked out of the nine planets?
Pluto, once the smallest and most distant planet, was removed from the solar system’s planet list in 2006 due to its tiny size, unusual orbit, and failure to meet new planetary criteria. Yet, Pluto remains a fascinating mystery, full of potential secrets that could reshape our understanding of the cosmos. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
The Sahara Dilemma: Are Deserts Vital to the Balance of Our Planet?
Deserts may seem lifeless, but they are vital ecosystems rich in biodiversity and cultural heritage. From storing carbon to nourishing distant rainforests, they play a key role in Earth's balance. Despite harsh conditions, both nature and humans have adapted, proving deserts are far more than dry, empty land. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
3 Important Novels You Should Read
3 Important novels that you should read more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
Are electric cars actually making sales? Which countries are leading the way?
Electric vehicles are growing fast, with countries like Norway and China leading the way. Backed by government incentives and better tech, they offer lower costs and cleaner air. While challenges like high production costs remain, EVs are becoming a smart, eco-friendly choice for the future. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
6 Things Expats Wish They Knew Before Moving to Hong Kong
Hong Kong’s street food scene is full of delicious surprises—think egg pancakes, wonton pasta, and authentic fish balls at wallet-friendly prices. If you’re feeling fancy, don’t miss the city’s Michelin-starred dim sum spots. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
Which determines whether it smells good or bad?
Your nose can detect thousands of scents thanks to millions of odor receptors, shaping your experiences and memories. Smells trigger emotional responses, connect to past events, and even signal danger—like the foul scent of rotten eggs. From birth, our genes and experiences guide how we react to different odors. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
Artificial Intelligence and the Future of Jobs: How to Adapt in the Age of Automation
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing how we work and live, creating exciting new job opportunities while reshaping old ones. As AI grows, jobs needing creativity and critical thinking will thrive, while routine tasks may vanish. Embracing continuous learning and adaptability is key to staying relevant in this fast-changing world. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
How to overcome your fear of flying
How to overcome your fear of flying more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
Nature's Fury: How Tornadoes Compare to Other Natural Disasters
Hurricanes unleash fierce winds and torrential rains that destroy homes, uproot trees, and cripple infrastructure. Their sheer power surpasses many other natural disasters, making early warnings, advanced technology, and public awareness vital to reduce their devastating effects on lives and property. more- ADVERTISEMENT