The Seven Years' War: A Global Conflict Defining a New Era
The Seven Years' War (1756-1763) was a huge conflict that spanned multiple continents and had far-reaching consequences for the future of world politics. Often seen as the first true "world war," most of the great powers of the time participated in it and reshaped the geopolitical landscape in profound ways. This article delves into the causes of the Seven Years' War, the main players, important events, consequences, and long-term consequences of the Seven Years' War.
Show key points
- The Seven Years' War, fought from 1756 to 1763, was the first global conflict involving major world powers across Europe, North America, India, and the Caribbean.
- Rooted in long-standing colonial rivalries and European power struggles, the war was sparked by tensions over territorial expansion and diplomatic alliances.
- Major nations such as Great Britain, France, Prussia, Austria, Russia, and Spain entered the war, each with distinct strategic goals and regional interests.
- ADVERTISEMENT
- In North America, known as the French and Indian War, pivotal battles like the Siege of Quebec and the fall of Montreal led to the collapse of French control in Canada.
- The war extended to Asia and the Caribbean, where British victories like the Battle of Plassey and the capture of French islands reinforced their imperial dominance.
- The 1763 Treaty of Paris marked the official end of the war, with Britain gaining vast territories and establishing itself as the dominant colonial power.
- Far-reaching consequences included shifts in global power, the rise of Britain and Prussia, and colonial unrest that would later fuel revolutions, notably in America.
The Seven Years' War was a pivotal moment in history, representing the first major global conflict that would lay the foundation for future international relations. This war was fought between 1756 and 1763, involving many of the world's most powerful nations, including Great Britain, France, Spain, Prussia, Austria, and Russia. The war was rooted in previous colonial and regional conflicts, fundamentally changing the balance of power in Europe and beyond.
Recommend
1. The causes of the Seven Years' War.
The origins of the Seven Years' War can be traced back to long-standing rivalries and struggles over territorial expansion and control. Several factors contributed to the outbreak of this conflict:
Colonial ambitions: The competition between Britain and France for colonial dominance in North America, the Caribbean and India was a major driving force.
European power struggles: In Europe, the war was rooted in the ongoing struggle for hegemony between the great powers, especially between Prussia and Austria for control of Silesia.
Diplomatic alliances: A complex network of alliances, such as the Anglo-Prussian Alliance and the Franco-Austrian Alliance, fueled the conflict.
2. Heroes of the Seven Years War.
Several major powers participated in the Seven Years' War, each with its own objectives:
Great Britain: sought to expand its colonial possessions and naval supremacy.
France: aimed to protect its colonies and counter British expansion.
Prussia: Under the leadership of Frederick the Great, it sought to preserve and expand its territory in Europe.
Austria: wished to regain Silesia and limit Prussian influence.
Russia: initially allied with Austria to reduce Prussian power but later changed alliances.
Spain: entered the war to protect its colonial interests and counter British influence.
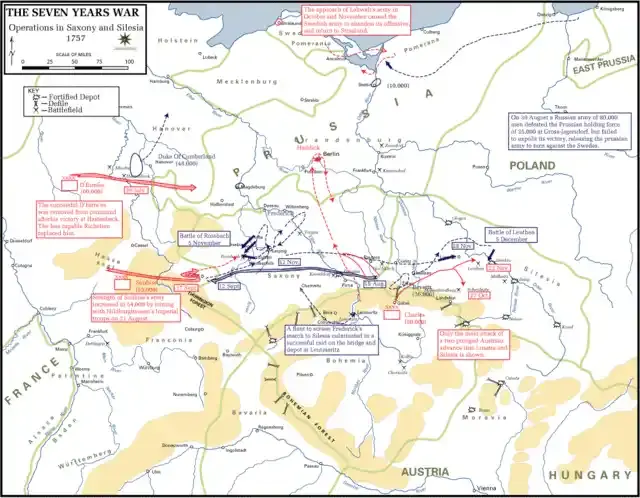
3. European Theater.

In Europe, the Seven Years' War was marked by many important battles and campaigns:
Battle of Rossbach (1757): Prussia, led by Frederick the Great, decisively defeated French and Austrian forces.
In Europe, the Seven Years' War was marked by many important battles and campaigns:
Battle of Rossbach (1757): Prussia, led by Frederick the Great, decisively defeated French and Austrian forces.
Russian campaigns: Russian forces initially achieved great successes against Prussia, capturing key territory.
4. North American Theater.
Known in North America as the French and Indian War, this theater saw a fierce conflict between British and French forces, along with their American Indian allies:
Battle of Fort Duquesne (1758): A decisive British victory opened the way for the conquest of Canada.
Siege of Quebec (1759): The British under General James Wolfe capture Quebec, marking a turning point in the war in North America
The fall of Montreal (1760): marked the end of French power in Canada.
5. Caribbean and India.
The Seven Years' War also spread to the Caribbean and India, where important battles over colonial possessions took place:
Battle of Plassey (1757): The British East India Company, led by Robert Clive, defeats Nawab Bengal, cementing British dominance in India.
Caribbean campaigns: The British captured several French islands, including Guadeloupe and Martinique, strengthening their colonial empire.
6. Winners of the Seven Years War.

The outcome of the Seven Years' War was largely favorable for Great Britain and Prussia:
Great Britain: Emerged as a prominent global colonial power, gaining large territories in North America, the Caribbean and India.
7. Treaty of Paris (1763).

The Treaty of Paris, signed in 1763, officially ended the Seven Years' War and redrew the map of the world:
Regional changes: France ceded Canada and territory east of the Mississippi River to Britain, while Spain ceded Florida to Britain in exchange for the return of Havana.
Colonial domination: Britain emerged as the dominant colonial power, while France retained some Caribbean islands and fishing rights off Newfoundland.
8. The repercussions of the Seven Years' War.

The Seven Years' War had profound and long-term effects on world politics and colonial relations:
British colonial policy: War expenditures prompted Britain to impose new taxes on its American colonies, sowing the seeds of discontent that eventually ignited the American Revolution.
Balance of power: The war reshaped the European balance of power, with Prussia and Britain emerging stronger, while the influence of France and Austria diminished.
Global conflicts: Paved the way for future global conflicts, as regional rivalries and ambitions continued to drive international relations.
The Seven Years' War was a defining moment in history that reshaped the world order and paved the way for future geopolitical developments. Its causes, key players, and important events underscore the complexity and far-reaching impact of this conflict. The outcome of the war and the subsequent Treaty of Paris not only redrew territorial boundaries, but also laid the foundation for future colonial and revolutionary movements, affecting the course of history for centuries to come.
![]()
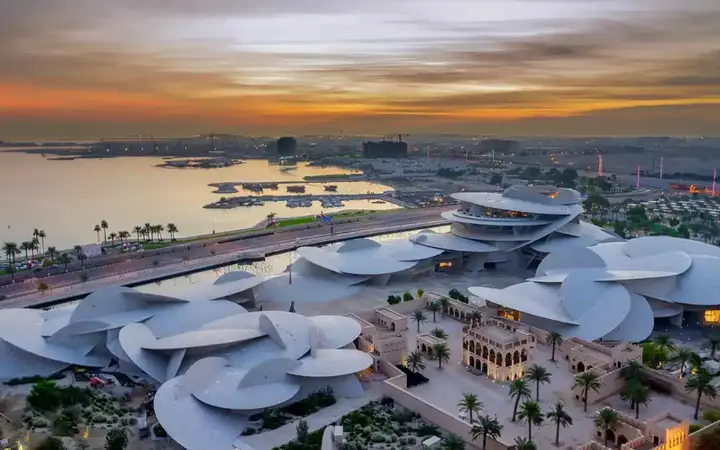
National Museum of Qatar and the distinctive design of the desert rose
The National Qatar Museum and its Unique Desert Rose Crystalline Structure more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
The cave beneath Pembroke Castle and the fate of the early Britons
A hidden cave beneath Pembroke Castle has revealed ancient secrets, including animal fats and tools that trace the journey of early Britons from hunters to farmers. This incredible find brings new light to prehistoric life and the evolving habits of those who lived beneath the castle centuries before it was built. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
What is the future of electric vehicles in the Arab world?
Electric vehicles are gaining ground in the Arab world as countries push for cleaner air, energy independence, and economic diversification. Governments like Saudi Arabia and the UAE are investing big, launching strategies, and building infrastructure to support EVs, while also partnering with global companies to boost innovation and job creation. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
Dubai Frame... Greatness lies in simplicity
Dubai Frame is a stunning landmark in Dubai offering breathtaking panoramic views from its transparent glass bridge. Visitors can journey through time with exhibitions showcasing Old Dubai, present-day marvels, and a futuristic vision of the city, all using immersive technology and interactive experiences—plus, coffee 150 meters above ground! more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
LI-FI: where the Internet travels at the speed of light
LI-FI, created in 2011 by Prof. Harald Haas in Scotland, uses light instead of radio waves for data transfer. It offers ultra-fast speed and strong security, making it ideal for sensitive environments. Despite its promise, challenges like high costs and dependency on constant lighting limit its widespread use. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
Blood test uses 'protein clock' to predict risk of Alzheimer's disease and other diseases
Blood test uses 'protein clock' to predict risk of Alzheimer's disease in others more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
How the nearby supernova left its mark on life on Earth
SN 1181, a mysterious "guest star" seen in 1181, has finally been linked to a rare supernova type called IAX. It left behind a "zombie" white dwarf, puzzling astronomers for centuries. New computer models now align with telescope data, offering fresh insight into this unusual celestial explosion. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
Human population growth: where are we now?
As the global population heads toward 10.5 billion by 2100, challenges like aging populations, food security, and environmental strain grow. While prosperity helps lower fertility, it also increases environmental harm. Addressing climate change, boosting food production sustainably, and shifting to low-carbon energy are key to balancing growth and the planet’s health. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
How to develop your self-confidence?: The journey of character building and self-development
Self-confidence is a powerful inner force that grows through experience, reflection, and personal development. It's not inherited but built over time. With positive thinking, healthy habits, and clear goals, anyone can strengthen their self-worth and face life with courage and resilience. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
Success Guide - How to Create Your Own Charisma?
Success Guide - How to Create Your Own Charisma? more- ADVERTISEMENT