What is the future of electric vehicles in the Arab world?
The Arab world is witnessing a growing interest in electric vehicles as a sustainable alternative to fossil fuel vehicles, driven by climate change concerns, rising oil prices and governments' desire to diversify energy sources. Arab countries offer incentives to attract investment in this area, such as tax breaks and the construction of charging stations.
Show key points
- The Arab world's growing interest in electric vehicles is driven by environmental concerns, fluctuating oil prices, and a push for energy diversification.
- Governments across the region are supporting the EV sector with incentives like tax exemptions and expanded charging infrastructure.
- Challenges such as limited infrastructure, high costs, and low public awareness still hinder widespread EV adoption.
- ADVERTISEMENT
- Key players like Saudi Arabia and the UAE are launching ambitious national strategies and setting production targets to boost EV integration.
- International collaborations with companies like Nissan and BYD are helping Arab nations build local EV manufacturing and development capabilities.
- Electric vehicles are seen as a tool to enhance energy security, reduce air pollution, and decrease reliance on non-renewable resources.
- Public and private sectors, along with increased consumer awareness, are expected to drive future growth in the Arab EV market, potentially reaching 3 million units by 203
The future of electric vehicles in the Arab world is very promising, but this requires overcoming some challenges, such as developing the necessary infrastructure, reducing costs, and raising awareness of their advantages. Thanks to the efforts of governments, businesses and consumers, electric vehicles are expected to play an important role in the future of transportation in the Arab world.
Recommend
In recent years, there has been growing growing interest in electric vehicles as a sustainable alternative to fossil fuel vehicles in the Arab world, which we can summarize in the following lines...
Why do Arab countries support the trend towards electric vehicles?

Mitigating climate change: Arab countries are striving to reduce carbon emissions, and electric vehicles are offering an effective solution to achieve this.
As a result, air quality improves, and emissions of fossil-fuel-powered cars contribute significantly to air pollution, posing a public health risk. Electric cars, which contribute to reducing air pollution and reducing greenhouse gas emissions, offer an environmentally friendly solution by reducing these harmful substances, thus improving public health and reducing respiratory diseases.
Reducing dependence on oil: Many Arab countries suffer from a shortage of oil resources or depend on importing it, which constitutes a significant economic burden. Electric vehicles offer a promising solution to reduce the energy bill by relying on local sources of renewable energy.
Energy security: Arab countries are seeking to reduce their dependence on oil and gas imports, and electric cars contribute to achieving energy self-sufficiency. This enhances energy security and saves money.
Electric vehicles can reduce the depletion of non-renewable natural resources, such as oil, contributing to long-term sustainability goals.
Creating new job opportunities: Stimulate investment in the manufacturing, development and operation of electric vehicles, creating new job opportunities.
What have Arab countries done to support the newcomer - electric cars?

Many Arab countries are making huge investments to the development of the electric vehicle sector, such as Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates. For example, Saudi Arabia has launched a national strategy for electric vehicles that aims to reach one million electric vehicles on the roads by 2030.
Efforts are being made by some Arab governments to encourage the use of electric vehicles by offering financial incentives and building appropriate charging infrastructure. Foremost among them are the Arab Gulf states.
National strategies: Some Arab countries are developing national strategies to promote the use of electric vehicles, such as Egypt and Morocco.
International partnerships: Arab countries are partnering with leading international companies in the field of electric vehicles, such as Nissan and the Chinese company BYD.
R&D support: Some Arab countries allocate budgets to support research and development in electric vehicle technologies.
Many Arab and international companies are involved in manufacturing and development projects in the region. For example, Saudi Arabia's NEOM is setting up a factory to manufacture electric cars, while Germany's Fox Group plans to start production in Morocco.
Increasing community awareness of its importance and benefits is noticeable. Awareness campaigns and media efforts contribute to spreading the culture of using these vehicles.
Electric vehicles - challenges and expectations:

Infrastructure: Most Arab countries lack the infrastructure needed to charge electric vehicles, such as charging stations.
Cost: Electric vehicles are still expensive compared to fossil fuel vehicles. Prices are still much higher, which is an obstacle to their purchase by large categories of consumers. It makes them inaccessible to all segments of society.
Lack of awareness of the importance of electric vehicles: Some consumers in the Arab world lack awareness of the advantages of electric vehicles. Unaware of its benefits or unconvinced of the feasibility of its use.
Despite the challenges, the future of electric vehicles in the Arab world is expected to grow significantly in the coming years. Studies show that electric vehicle sales in the region could reach 3 million units by 2030.
The future of electric vehicles in the Arab world requires a joint effort from governments, businesses and civil society to ensure the rapid and effective deployment of this technology.
![]()
The best professional advice (in life) one can get
Choosing the right career can be tough, but combining self-assessment, research, and goal-setting with expert guidance makes the path clearer. Tools like MBTI and career mentors help align your job with your values, making your professional journey both successful and fulfilling. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
Journey to Mars: The Next Great Leap in Mankind's Quest for Discovery
Mars sparks human curiosity like no other planet—its Earth-like features, potential for life, and promise of resources fuel hope for a future civilization there. Despite daunting technical, environmental, and psychological challenges, global efforts aim to turn this bold dream into reality. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
Unbelievable Interference of AI! Including garbage analysis!
From analyzing garbage to find eco-solutions, to helping a man find his wife, and even powering electric shoes that boost your walking speed—AI is doing some unbelievable things! These creative uses show just how far artificial intelligence can go beyond traditional boundaries. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
The Ultimate Swallowers: Exploring the Voracious Nature of Black Holes
Black holes are mysterious giants with immense gravity that swallow everything—even light—making them terrifying and fascinating. With their super-powerful pull and potential to distort space-time, they capture scientists’ and dreamers’ imaginations. Are they evil forces or just strange cosmic rules at play? The mystery continues to deepen. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
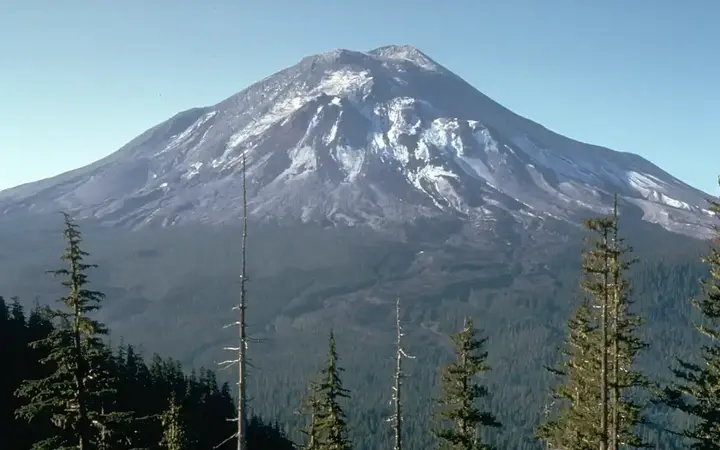
Mount St. Helens blast and rebirth
Mount St. Helens, once shattered by a deadly eruption in 1980, now stands as a powerful symbol of nature's recovery. From barren ash fields to thriving ecosystems, it shows how life returns. Today, it draws visitors eager to witness Earth’s healing and learn from its remarkable transformation. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
Artificial Intelligence and the Future of Jobs: How to Adapt in the Age of Automation
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing how we work and live, creating exciting new job opportunities while reshaping old ones. As AI grows, jobs needing creativity and critical thinking will thrive, while routine tasks may vanish. Embracing continuous learning and adaptability is key to staying relevant in this fast-changing world. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
Navigating the Chaos: From Chaos to Stability in Life
Chaos is a natural part of life, often unavoidable but not unmanageable. With tools like mindfulness, time management, and support systems, individuals can reduce its impact and find stability. It's less about eliminating chaos and more about adapting to it wisely for a more balanced life. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
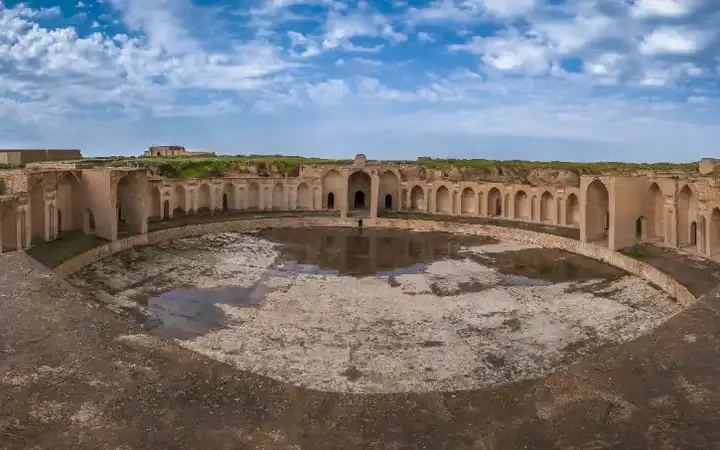
The history of the city of Samarra ... Iraq's Hidden Gem
Samarra, once a grand Abbasid capital, still stands with its iconic spiral minaret and rich Shia heritage. Though chosen as the capital of Islamic civilization in 2020, the city remains dusty and neglected, holding untold stories within its historic ruins. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
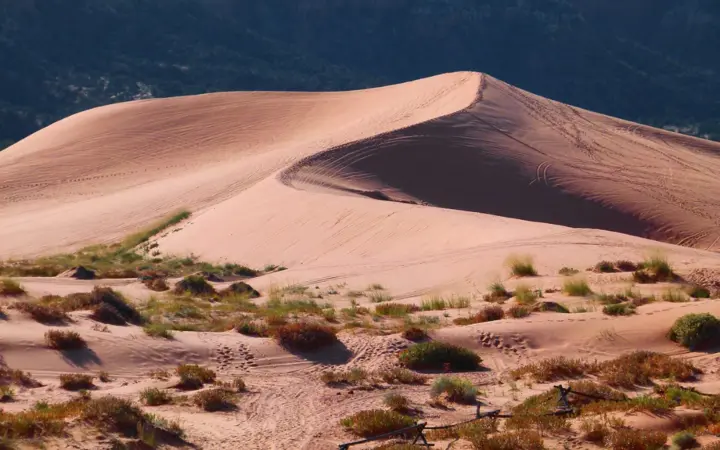
Discover the Impossible: Turning Deserts into Dense Forests – Dream or Reality?
Desert greening is turning deserts into lush forests using smart water techniques, solar and wind farms, and fertile soil solutions like pyrogenic carbon. Projects like the Sahara Forest Project aim to fight drought, boost agriculture, and even combat climate change, turning drylands into thriving ecosystems. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
You can train your brain to increase your attention span, and here's how
Distractions are everywhere, but by building better habits—like getting enough sleep, keeping your phone out of reach, and taking mindful breaks—you can train your brain to stay focused longer and boost your productivity throughout the day. more- ADVERTISEMENT