A piece of the earth's crust is missing, and scientists are discovering its whereabouts!
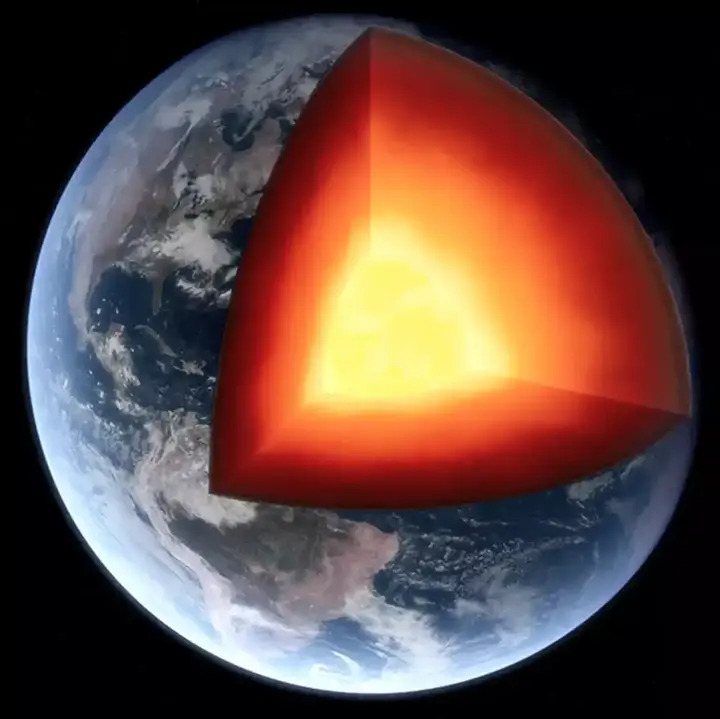

In a startling discovery, scientists have recently been able to locate a missing part of Earth's crust, a discovery that holds significant implications for our understanding of the planet's geological history and the dynamic processes that occur in it. The search for this missing part has spanned decades, using advanced techniques, meticulous research and a constant curiosity that stimulates scientific exploration.
1) The puzzle of the missing shell

The earth's crust is the complex and dynamic outer layer made up of continental and oceanic plates. These plates are constantly moving due to tectonic activity, leading to phenomena such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and the formation of mountain ranges. Over geological time, one tectonic plate can slide under the other, and this ongoing process can sometimes hide the locations of large pieces of crust, making it difficult for geologists to compile the history of the planet.
Recommend
For many years, scientists have been confused about a large "missing" part of Earth's crust, one that seems to have disappeared without a trace. This mystery has been the subject of intensive study, as locating this lost crust can provide important insights into the tectonic processes and geological development of our planet.
2) The Great Discovery
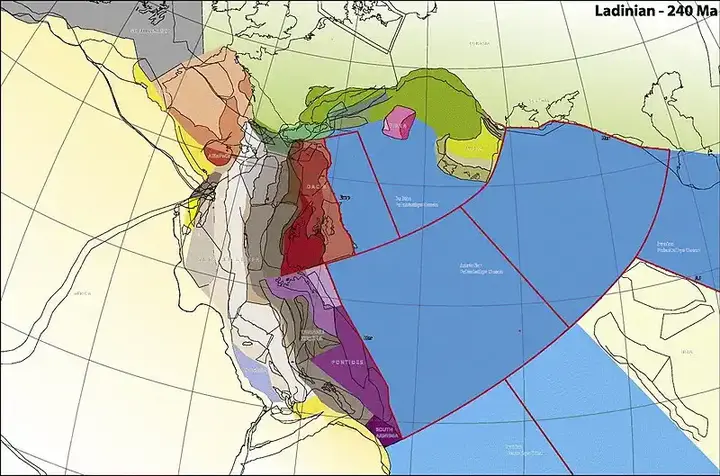
The breakthrough occurred when a team of geologists, using advanced seismic imaging technology, identified a vast submerged area in the Indian Ocean. This area, known as the "Greater Adria", was discovered as a missing part of the mystery. Greater Adria is an ancient small continent that existed about 140 million years ago, during the time of the dinosaurs. It was located between African and Eurasian tectonic plates, and spans what is now the Mediterranean.
By carefully analyzing seismic waves caused by earthquakes, scientists were able to draw the structure of the crust beneath the Indian Ocean. Their results showed that the Great Adria had been gradually sinking beneath the Eurasian plate over tens of millions of years. This process effectively concealed the small continent, as it was buried deep inside the earth's mantle.
3) Decipher geological puzzles
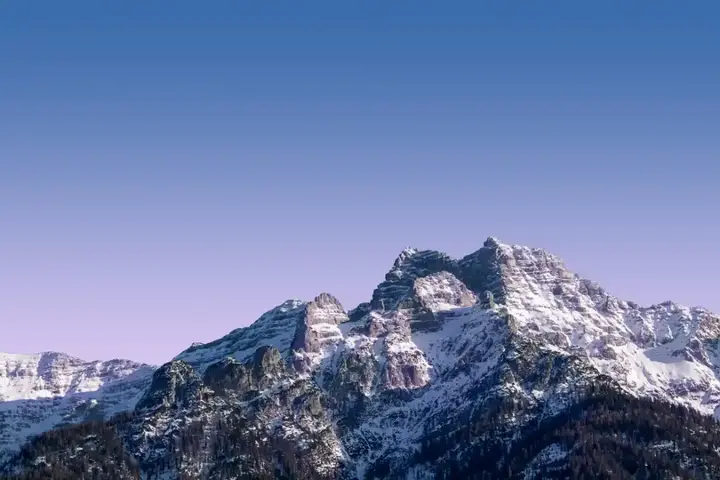

The discovery of Greater Adria not only solves the mystery of the lost crust, but also sheds light on the complex geological history of the Mediterranean region. About 140 million years ago, Greater Adria was a large tropical landmass covered with shallow seas and coral reefs. It broke away from the supercontinent Gondwana and began its journey northward, colliding with the Eurasian plate.
As she moved, the Great Adria was slowly immersing herself in the subduction process, causing her to sink into the mantle. This tectonic voyage led to the formation of mountain ranges, such as the Alps, where parts of the Great Adria were scraped and accumulated on the Eurasian plate. The remains of this small continent are still present in these mountain ranges today.
4) Implications for geology and beyond
The discovery of Greater Adria has profound implications for the field of geology, as it provides a rare opportunity to study tectonic and subduction processes in detail, providing insights into how continents evolve and interact over geological time. This knowledge can help scientists better understand the forces that make up our planet and predict tectonic activity in the future.
Moreover, the findings have broader implications for the exploration of natural resources. In fact, understanding the geological history of areas where the remains of the ancient crust are found can help in the search for precious metals and fossil fuels. The remains of the Adria, for example, may contain untapped reserves of these resources.
5) Technological advances in earth sciences
The discovery of the Great Adria highlights the importance of technological advances in the field of earth sciences. Seismic imaging has revolutionized our ability to look deep into the ground and uncover hidden geological features. By analyzing how seismic waves travel through different layers of the Earth, scientists can create detailed images of the inner layers, just as computed tomography provides a look inside the human body.
In addition, this discovery highlights the collaborative nature of modern scientific research. The study involved geologists from different countries, combining their expertise and resources to solve a complex geological puzzle. This international cooperation is essential to enhance our understanding of the Earth and address global challenges.
6) Lessons learned and the future

This great discovery of the Greater Adria opens up new horizons for our scientific understanding and emphasizes the importance of scientific research and international cooperation. Our understanding of our planet is still in its infancy, and each new discovery adds a layer of knowledge and helps us make progress.
As technology continues to evolve, we can expect more exciting discoveries about Earth's structure and internal processes. This scientific journey is not only about uncovering the mysteries of the Earth, but also about using this knowledge to improve our lives on the surface, by predicting natural disasters and managing resources more efficiently.
7) Similar story

Another mystery that has puzzled experts for more than a century has been known as the "Big Difference" and refers to large slabs of Earth's crust that were missing from the geological record in that the age of the rocks changes sharply due to the erosion of previous rocks that are then replaced by newer rocks, producing a gap in the sedimentary record. This phenomenon was first observed in 1869 in the Grand Canyon, Arizona in the United States, however, new evidence has shown that the disappearance of these plates may be due to severe ice erosion that occurred during a period known as the "snowball" when the entire planet was covered in ice.
8) Conclusion

In conclusion, the discovery of the missing part of the Earth's crust, identified as the small ancient continent of Greater Adria, is a remarkable achievement that enhances our understanding of the planet's geological history. It shows the power of modern technology and collaborative research in deciphering the mysteries of our world. As scientists continue to explore the depths of Earth's crust, we can expect more exciting discoveries about the dynamic processes that have shaped – and continue to shape – our planet.
![]()
The world of Arab game developers - independent and unknown successes
Arab games developers - Unknown independent Successes more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
How is Dubai developing a farm in the heart of the desert?
Dubai is turning desert into farmland using hydroponics and vertical farming, creating a green oasis in harsh conditions. This bold project boosts food security, reduces water use, and embraces clean energy—showing the world how innovation can grow crops where none thought possible. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
For an unforgettable photo – your simplified guide to professional photography with minimal potential
For an unforgettable photo – your simplified guide to professional photography with minimal potential more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
Things people with emotional intelligence never do
Emotional intelligence helps people understand and manage emotions, leading to better relationships, improved teamwork, and stronger mental health. It can be developed through self-reflection, mindfulness, and active listening. Emotionally intelligent people avoid impulsive actions and build balanced lives with better decision-making and communication. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
Habits of remarkably calm people
Remarkably calm people aren't born that way—they build habits like mindfulness, deep breathing, and regular exercise to stay composed. They also focus on positive thinking, good sleep, and managing time well. These simple yet powerful habits help them stay cool even when life gets stressful. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
The most expensive mistakes in history
The most expensive mistakes in history more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
The Power of Nature: Learn about the forces behind a living volcano
Living volcanoes are powerful natural wonders—windows into Earth’s fiery depths. They dazzle with beauty, yet threaten with eruptions. From shaping landscapes to offering geothermal energy, they reveal nature’s immense force. By studying their behavior, we can better predict their eruptions and harness their energy for a safer, sustainable future. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
Explore the magic of Belfast: from ship history to contemporary art culture
Belfast blends rich shipbuilding history with vibrant culture, stunning modern architecture, and lively arts. From Titanic’s legacy to music festivals and scenic parks, the city offers unforgettable experiences. Stroll markets, enjoy local dishes, and soak in the warmth of a place where tradition meets creativity. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
First Steps to Investing: Practical Tips to Build Your Wealth
Starting your investment journey? Learn the basics, explore different asset types, and build a balanced plan tailored to your goals and risk tolerance. Stay patient, diversify wisely, and avoid common mistakes like investing with borrowed money. Smart moves now can shape a brighter financial future. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
The world's oceans: species, environments, life and the magic of colors
The oceans, covering over 70% of Earth, are changing color due to climate change and human impact. From deep blue in the Pacific to green or milky turquoise in coastal or Arctic waters, these shifts reveal changes in marine life and health, making ocean conservation more vital than ever. more- ADVERTISEMENT





















