Why can't bots click on the "I'm not a robot" box on sites?
It has become customary in the online world to see checkboxes asking us to confirm that we are not robots. These boxes, which contain the phrase "I'm not a robot," are part of a system called reCAPTCHA, which aims to protect sites from unwanted activities. The reCAPTCHA system is based on several complex technologies to confirm the identity of users and whether they are humans or robots. But the question remains: why can't robots simply click on this box and pass without problems? In this article, we will review the technical reasons behind this and how these systems work in ways that protect sites and ensure the security of users. We will explore the evolution of CAPTCHA, how reCAPTCHA works, as well as the hidden methods the system uses to analyze users' behavior. We will also address the challenges facing these systems in the future as artificial intelligence evolves and robots become more capable of performing complex tasks. The goal is to provide a comprehensive understanding of how these systems work and their importance in keeping the internet safe.
Recommend
Evolution of the CAPTCHA verification system
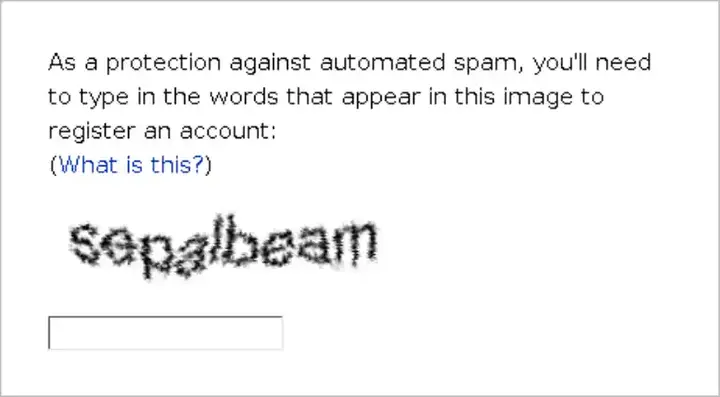
It has evolved significantly over the years. Initially, tests relied on providing blurry text that was difficult for robots to read, but with the advancement of artificial intelligence, robots were able to pass these tests easily. As a result, it was necessary to develop more complex verification systems. Google has acquired the reCAPTCHA system, which adds a new level of complexity and effectiveness in tackling bots. reCAPTCHA relies on analyzing user behavior rather than just presenting cluttered texts. This technique depends on several factors, such as click speed, mouse motion path, and reaction timing. Thanks to this development, it has become difficult for conventional robots to bypass these systems. But that doesn't mean the challenge is over. Systems need to be constantly updated and developed to keep pace with advances in artificial intelligence and robotics technologies.
How does reCAPTCHA work?

The reCAPTCHA system not only relies on the user's ability to click on the box, but also monitors how the user clicks and the user's behavior during it. Robots are usually faster and more efficient than humans at performing tasks, including clicking on squares. The system analyzes the mouse's trajectory and click speed, as humans are usually slower and more random in their movements. If the click is too fast and direct, the system asks the user to complete an additional test such as recognizing certain images. These additional tests rely on the user's ability to recognize elements in images, a task that is still difficult for robots due to the complexity of the images and overlapping visual factors. Thanks to these technologies, reCAPTCHA can distinguish between humans and robots with high accuracy, helping to protect sites from unwanted activities.
Hidden methods and comprehensive surveillance
Some sites now use invisible verification technologies, which analyze user behavior on the Internet such as mouse path, browsing history, and cookies. These systems give users scores based on available information to determine whether they are humans or robots. Although these technologies may seem invasive to privacy, they help keep the user experience smooth and secure. The reCAPTCHA Enterprise system, for example, relies on a wide range of data to provide accurate estimates about a user's identity. A variety of factors are analyzed, such as how you navigate between pages, interact with content, and even write speed. This information is collected and analyzed in real-time to ensure that the user is real and not a robot. Thanks to these advanced methods, reCAPTCHA can provide an extra layer of security without significantly compromising the user experience.
The future of verification regimes and their challenges

As AI continues to evolve, some robots are able to pass complex Turing tests, creating significant challenges for existing verification systems. This development forces developers like Google to devise more complex and effective solutions in distinguishing between humans and robots. For example, we may need verification systems that rely on deep analysis of human behavior in more complex ways, such as typing pattern analysis, and the use of artificial intelligence to understand the context in which sites are interacting. These developments could include the use of deep learning and neural networks to analyze real-time data and provide accurate assessments of user identity. In addition, future solutions could include facial recognition technology or even biometric analysis as an additional means of identity verification. But with all these developments, there also comes the challenge of maintaining users' privacy and ensuring that personal data is not used in unethical ways. Therefore, there must be a careful balance between security and privacy, which requires constant collaboration between technology developers and legislators to ensure the best results. Ultimately, verification systems remain a key element in keeping the internet secure, but they must remain flexible and sophisticated to meet future challenges.
In the end, there's no magic reason why bots can't click on the "I'm not a robot" box, it's about how to click. Current systems rely on the analysis of random and slow human behavior compared to fast and accurate robotic behavior. As AI evolves, we will always need to update verification systems to ensure online security.
![]()
Time Management Skills: Effective Methods to Increase Productivity
Time isn’t just ticking—it’s the most valuable thing we have. Managing it right means less stress, more focus, and better balance between work and life. With simple techniques like prioritizing tasks or using the Pomodoro method, we can work smarter, not harder, and truly make every moment count. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
Moving forward still represents progress: trusting the process and taking my own best advice
Moving forward still represents progress: trusting the process and taking my own best advice more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
What is the coldest place in the solar system?
The coldest natural spots in our solar system might be double-shaded craters at the Moon’s south pole, with temperatures around 25 K—colder than Pluto. These craters avoid all sunlight, trapping extreme cold for billions of years and possibly preserving water ice and other volatile compounds. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
Best Graphic YouTube Design Learning Channels in Arabic
Noor Design Channel stands out by teaching design basics like color theory in a hands-on way, helping many Arabs become skilled designers. It also guides learners on turning design skills into freelance work, making it a top pick for Arabic-speaking beginners. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
Motivation: How to Start and Stay Motivated
Motivation: How to get started and staying motivated more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
Medieval Viking banquets
Medieval Viking banquets more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
Does pregnancy accelerate "biological aging"?
A study in the Philippines found that pregnancy may speed up biological aging in women, with each pregnancy linked to about 4 to 4.5 months of aging. This effect wasn't seen in men, and varied depending on context. Researchers hope these insights might guide future anti-aging treatments. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
How does fear work? What is phobias?
How does fear work? What is phobias? more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
Can you really master a skill by learning for one hour a day?
Can You Really Master a Skill by Learning for One Hour a Day? more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
If we look at Olympic stadiums since 1896, are they still in use?
Looking back at the Olympic venues since 1896 – are they still in use more- ADVERTISEMENT





















