History of the Panama Canal: everything you need to know
The Panama Canal is one of the greatest engineering achievements of the twentieth century, connecting the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans and shortening thousands of miles of cruises. Thanks to this canal, ships can easily move between the two oceans without having to go around South America. The idea of building the canal began in ancient times, but the project was not implemented until the early twentieth century. In this article, we will review the history of the Panama Canal, from the first idea to its vital role in today's global trade.
Show key points
- The Panama Canal is a major engineering marvel that connects the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, drastically reducing maritime travel distances.
- Although the concept of building a canal dates back to the 16th century, it wasn't realized until the 20th century due to technical and financial obstacles.
- France's initial attempt under Ferdinand de Lesseps failed due to deadly tropical diseases and financial collapse.
- ADVERTISEMENT
- The United States took over the project in 1904, overcoming disease and engineering challenges to complete the canal in 191
- The canal revolutionized global trade by offering a faster, more cost-effective route for shipping between oceans.
- Economically, the canal boosts Panama’s revenue through tolls, supports job creation, and strengthens global trade networks.
- The 2016 expansion, featuring new locks for larger ships, enhanced the Panama Canal's capacity and reinforced its global strategic importance.
Beginning: Early Idea and Initiatives

A canal between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans has been in place for centuries, as Europeans have been thinking of ways to facilitate the movement of ships between the two oceans without having to circumvent South America. In the sixteenth century, Spanish explorers proposed the idea of a canal across the Isthmus of Panama, but technical and financial challenges made the idea impossible to implement at the time. In the late nineteenth century, France undertook the first serious attempt to build the canal under the leadership of the engineer Ferdinand de Lesseps, who had succeeded in building the Suez Canal. Despite the great ambition, the French project faced catastrophic financial and health problems. Tropical diseases such as malaria and yellow fever killed thousands of workers, and with dwindling financial resources, France faltered and construction halted in 1889. After the French failure, the United States took over the project at the beginning of the twentieth century after signing a treaty with Panama. The works began in 1904 under the direction of engineer John Stevens, who solved many engineering and financial problems. The sanitary conditions of workers have also been improved thanks to significant efforts to combat tropical diseases. Thanks to these improvements and careful planning, the United States was able to complete the project that the world has long dreamed of, becoming a reality.
Recommend
Achievement: Construction and Challenges
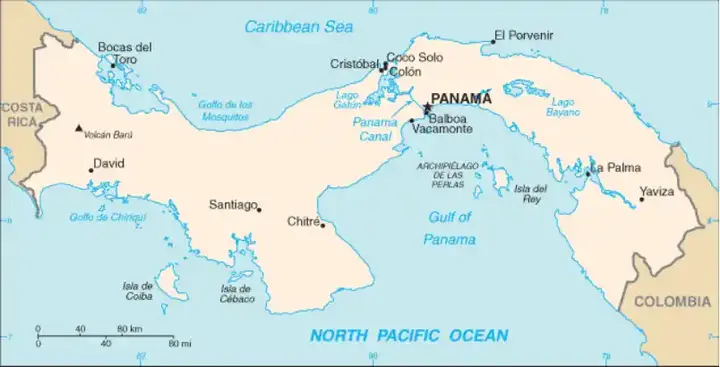
Engineering challenges in history, which included digging vast amounts of soil and rock and building huge locks to regulate the passage of ships. The United States used advanced engineering techniques and overcame many obstacles, including tropical diseases such as malaria and yellow fever, which were killing workers. The works began with the excavation of a wide and deep channel across the isthmus, and included the construction of three sets of locks on both sides to lift ships to the artificial Gatun Lake. These locks, considered one of the greatest achievements of civil engineering, allow ships to overcome the difference in water altitude between the two oceans. Engineer George Washington Gothales had a crucial role in leading the project to success. Besides the engineering challenges, there were logistical and financial challenges, as the project required careful organization and the provision of huge resources. Despite all these challenges, the construction of the canal was completed in 1914, and officially opened on August 15 of the same year. The construction of the Panama Canal is a great engineering achievement that has contributed to strengthening the United States' position as a global industrial power, as well as facilitating maritime trade between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans.
Economic and trade impact
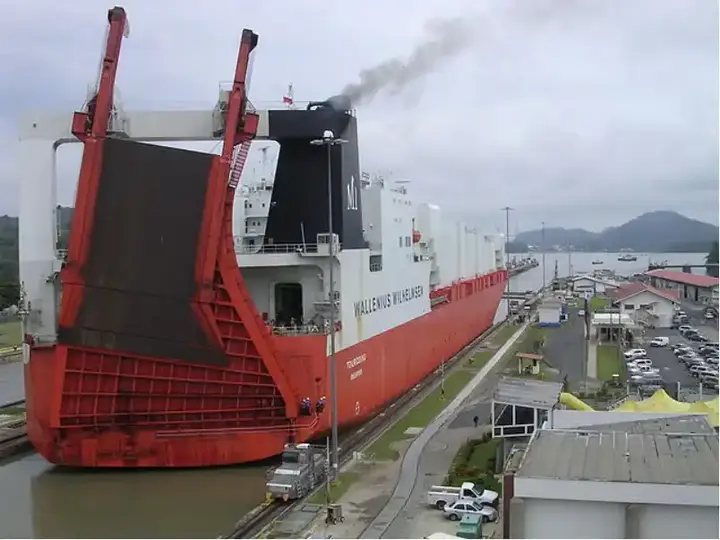

The Panama Canal radically transformed global trade, becoming a vital shipping lane between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans. Before the canal opened, ships had to circumvent Cape Horn in the far south of South America, greatly increasing the time and cost of cruises. Thanks to the Panama Canal, distances were significantly shortened, reducing the cost of shipping and increasing the efficiency and speed of maritime trade. Today, hundreds of ships pass through the canal daily, carrying goods and raw materials between the continents of the world, making it one of the most important waterways in the world. The Panama Canal plays a vital role in the global economy, facilitating the transport of goods and the flow of trade between various global markets. It is also a major source of income for Panama, where tolls are collected for ships that transit through it. These fees are used for the maintenance and operation of the canal, as well as in supporting the local economy. The impact of the canal also extends to job creation and economic growth in the region. Thanks to the Panama Canal, global trade has become more efficient and faster, enhancing trade cooperation between countries and contributing to global economic growth.
Recent expansions and updates
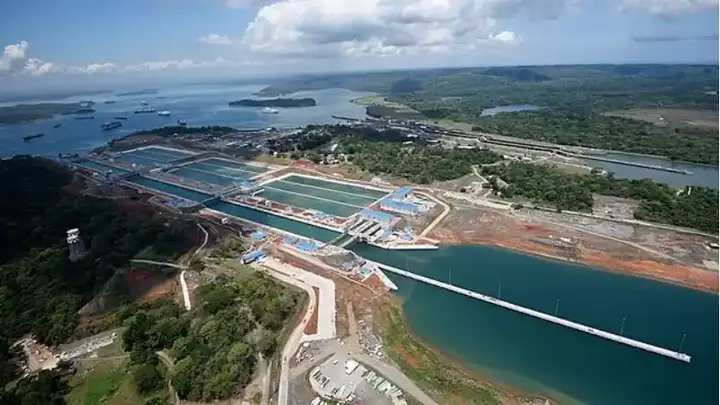

Over time, the need to expand and modernize the Panama Canal has become essential to keep pace with the increase in shipping traffic and the evolution of ship size. In 2007, the canal expansion project was initiated, which was completed in 2016. The expansion included the construction of a new set of locks, allowing the passage of larger ships and increasing the capacity of the canal. These recent improvements have contributed to strengthening the canal's role as a vital nerve in global trade and increasing its efficiency in dealing with intensive maritime traffic. Thanks to these expansions, the Panama Canal continues to serve efficiently and effectively, reinforcing its position as a strategic global waterway.
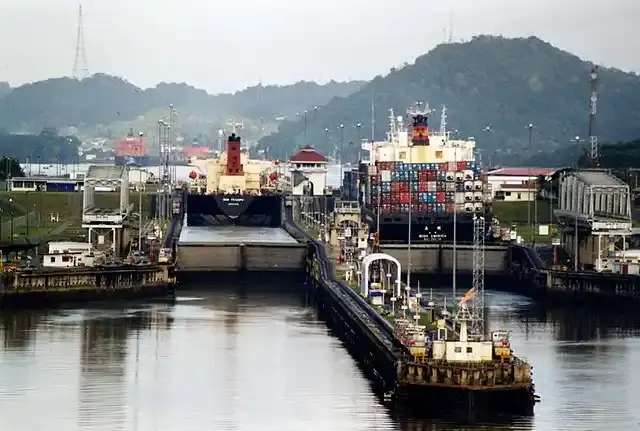

In conclusion, the history of the Panama Canal is full of challenges and achievements, from the first idea to its current role as one of the most important waterways in the world. Thanks to significant engineering efforts and continuous upgrades, the Panama Canal remains vital in boosting global trade and facilitating maritime transport between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans. Understanding the history of this great canal gives us a deep insight into the engineering progress and commercial development that humanity has witnessed throughout the ages. Thanks to the Panama Canal, global trade has become more efficient and faster, contributing to the strengthening of the global economy and cooperation between nations.
![]()
Shocking fact: the moon is moving away from the earth!
The Moon is slowly drifting from Earth—about 3.8 cm a year—thanks to tidal friction. This tiny shift, tracked since NASA's Apollo missions, may eventually lengthen our days. Don't worry though; the Moon won't escape. It'll settle into a stable distance over time. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
At each moment, there are about 2,000 thunderstorms occurring on Earth.
Thunderstorms are powerful and common, with up to 2,000 happening worldwide at any time. Florida sees the most in the U.S., while Venezuela’s Lake Maracaibo holds the record for lightning. Remember: if you hear thunder, go inside—lightning can be deadly, even from miles away. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
Sand and fog skies: a harsh introduction to Mauritania
Nouadhibou may appear harsh and chaotic, yet its dusty markets and joyful children reveal a community full of resilience and warmth. Despite poverty and challenges, the city radiates human spirit and hope, offering visitors an unforgettable glimpse into a life built on adaptation and cooperation. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
What is the coldest place in the solar system?
The coldest natural spots in our solar system might be double-shaded craters at the Moon’s south pole, with temperatures around 25 K—colder than Pluto. These craters avoid all sunlight, trapping extreme cold for billions of years and possibly preserving water ice and other volatile compounds. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
The biggest mystery in geology - when plate tectonics began to reshape the Earth
On February 6, 2023, a powerful earthquake struck the eastern Mediterranean, shifting the Anatolian Peninsula by 11 meters and killing nearly 60,000 people. This disaster highlights how tectonic plate movements reshape Earth's surface and cause devastating quakes by releasing built-up pressure at plate boundaries. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
The most impressed Japanese techniques in modern times
Japan keeps surprising the world with weird yet useful inventions—like heated toilet seats and noise-canceling forks. One standout? Healthcare robots that assist the elderly, making life easier and healthcare smarter. Also, karaoke, born in Japan, totally changed entertainment. It's clear: Japan knows how to mix fun, tech, and innovation. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
The strange long history of Teflon: the non-subversible product that nothing sticks to
The Long, Strange History of Teflon: The Indestructible Product Nothing Seems to Stick To more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
The dark side of remote work that no one talks about: it's not just about wearing sweatpants and flexibility
Remote work may seem dreamy, but loneliness, blurred boundaries, and snack-fueled sofa days can take a toll. You might miss office perks, relationships, and even your boss forgetting you exist. It’s not all bad—but it’s not all good either. Just remember to move, unplug, and please, wear pants on video calls. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
How food and pH affect the action of drugs in the body
How food and pH affect the action of drugs in the body more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
3 Important Novels You Should Read
3 Important novels that you should read more- ADVERTISEMENT





















