Islamic Hijri calendar – its history, uses and possible improvement
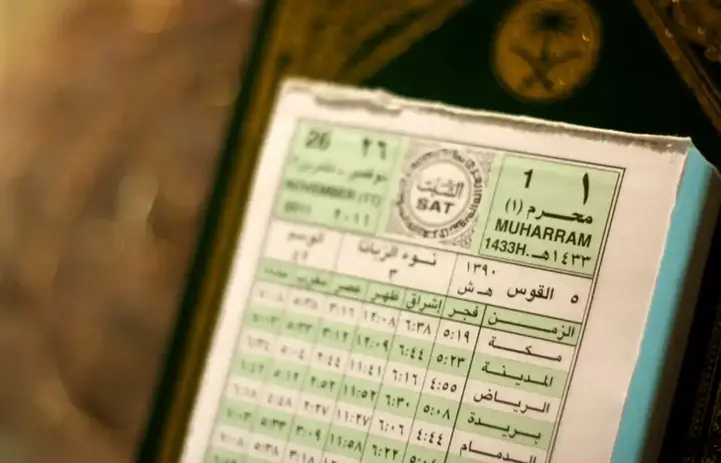
The Hijri calendar, also known as the Islamic or lunar calendar, has profound significance for Muslims around the world. This article aims to delve into the history and importance of the Hijri year, the traditions surrounding it, and review its reliability and the possibility of improving it using modern science.
Show key points
- The Hijri calendar, initiated in 622 CE with the Prophet Muhammad's migration to Medina, serves as both a historical milestone and spiritual foundation for Muslim identity.
- Comprising 12 lunar months like Ramadan and Dhu al-Hijjah, the Hijri calendar marks religious events and offers Muslims spiritual opportunities throughout the year.
- Celebrations of the Hijri New Year involve diverse cultural practices—such as prayer, charity, and family gatherings—highlighting communal bonds and religious reflection.
- ADVERTISEMENT
- While firmly rooted in religious tradition, the Hijri calendar's accuracy is sometimes challenged by regional disparities in moon sighting methods and interpretation.
- Modern astronomical tools can enhance the Hijri calendar's reliability by providing consistency in month calculations and facilitating calendar alignment across Muslim communities.
- Predominantly used in Muslim-majority countries like Saudi Arabia, Egypt, Pakistan, and Indonesia, the Hijri calendar maintains a global presence through religious observances.
- Though spiritually rich and symbolically significant, the Hijri calendar faces practical drawbacks in daily life due to its misalignment with the solar year and global time systems.

Date and importance of the Hijri calendar:
The Hijri calendar, which began with the migration of the Prophet Muhammad from Mecca to Medina in 622 CE, is a pivotal aspect of Islamic history. This migration is not only a physical journey, but also symbolizes the spiritual and political transformation of Muslim society. Recognizing the need for a calendar in line with Islamic months and events, Muslim scholars and companions of the Prophet devised the Hijri calendar. Its adoption was not only a practical measure, but also a declaration of the distinct identity and sovereignty of the Islamic Ummah. The Hijri calendar is more than just a time mark; it sums up the spiritual and cultural spirit of Islam, as it provides Muslims with a framework for regulating religious duties, guiding them through the rhythm of fasting during Ramadan, pilgrimages to Mecca, and the celebration of other important dates such as Eid al-Fitr, Eid al-Adha, and the Prophet's birthday. Moreover, the Hijri calendar fosters a sense of unity among Muslims around the world, transcending geographical and cultural boundaries where believers come together in observance of common religious practices.
Recommend
Islamic Months:
The Hijri calendar consists of 12 lunar months, each of which has its own historical and religious significance. From Muharram, the first month and the majestic period of meditation, to Ramadan, the ninth month and the time of spiritual renewal through fasting, each month presents unique opportunities for spiritual growth and connection with God. Twelfth month, Dhu al-Hijjah peaks in the Hajj season and symbolizes the unity and diversity of the global Muslim community as millions converge to worship at the holy sites of Islam.
Traditions and practices:
The advent of the Hijri year is characterized by a tapestry of religious rites and cultural traditions that vary across Muslim-majority regions. In many communities, this occasion is characterized by prayer, recitation of Quranic verses, and doing good deeds and giving. Families gather for festive meals, exchanging congratulations and gifts as they celebrate the beginning of a new year full of hope, faith and blessings. The cultural richness and diversity of Islamic traditions are embodied in the myriad ways in which Muslims celebrate the Hijri year, reflecting the multifaceted fabric of the global Muslim Ummah. When Muslims embark on another Hijri year, they engage in a period of reflection and renewal. The transition to a new year prompts reflection on past actions, gratitude for the blessings received, and aspirations for personal and spiritual growth in the year ahead.
When was it placed as a reference in Islamic culture?

The establishment of the Hijri year as a reference year in Islamic culture dates back to the early Islamic era, specifically to the year 622 AD. The decision to adopt the Hijri calendar as the reference year in Islamic culture was taken shortly after the migration to Medina. The Islamic lunar calendar, based on lunar cycles, was chosen to align it with lunar months and events of Islamic significance. The migration to Medina signaled not only the beginning of a new phase in the life of the Muslim community, but also the establishment of a political and religious center for Islam. The migration to Medina brought great changes to the life of the early Muslim community, including the establishment of a new social order, the formation of alliances with local tribes, and the implementation of religious and legal practices. The Hijri calendar served as a practical tool to regulate these developments and became a symbol of the distinct identity and sovereignty of the Islamic Ummah.
Is it reliable?
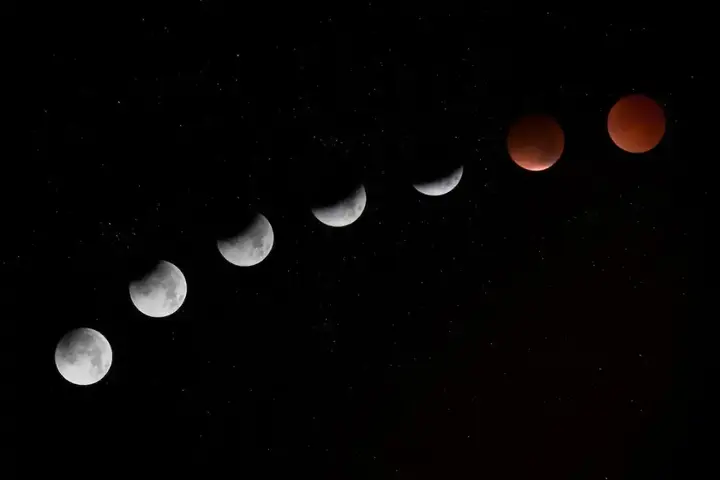

The reliability of the Hijri calendar depends on various factors, including its accuracy in determining lunar months, consistency of crescent sighting practices, and adherence to traditional methods of calculation. Here are some considerations related to the reliability of the Hijri calendar:
Lunar months and crescent sighting:
The Hijri calendar is based on the lunar cycle, with the months beginning when the new moon is sighted. The determination of the beginning of each Islamic month depends on the sighting of the crescent, which can vary depending on factors such as geographical location, weather conditions, and clarity of the sky. This discrepancy in moonsight practices can sometimes lead to discrepancies in the start dates of Islamic months between different Muslim communities.
Traditional calculation methods:
Historically, the Hijri calendar has been calculated using traditional methods based on lunar observation and mathematical calculations. These methods have evolved over time and may vary between scholars and Muslim communities. Efforts have been made to standardize the calculation of the Islamic calendar, but differences in interpretation and methodology continue to lead to differences in the identification of the start dates of Islamic months and religious ceremonies.
Rounding and adjustment:
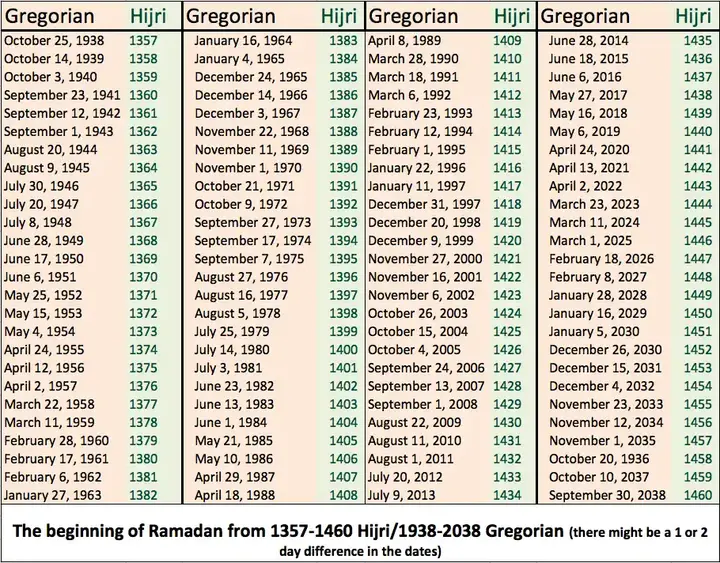
To reconcile the shorter lunar year in the Hijri calendar with the longer solar year in the Gregorian calendar, different adjustment methods were used, such as rounding. However, these amendments are not universally applied, and there may be differences between Muslim societies regarding the inclusion of additional days or months (such as a leap year) to align the lunar calendar with the solar calendar. This can affect the accuracy and consistency of the Hijri calendar over time.
Can astronomical calculations improve its uses?
Yes, astronomical calculations can play an important role in improving the accuracy of the Hijri calendar and facilitating its use. Here are some ideas for that:
Predictability of lunar months:
Astronomical calculations can accurately predict the beginning of each lunar month based on the movement of the Moon. By calculating how well the crescent is visible and associated with specific celestial signs, astronomers can more accurately determine the beginning of Islamic months. This reduces reliance on local crescent sighting practices, which can vary and sometimes lead to discrepancies in determining the beginning of the month.
Consistency in calculating the calendar:
Traditional methods of calculating the Hijri calendar may differ between Muslim communities and scholars, leading to differences in determining the start dates of Islamic months. Astronomical calculations provide a unified methodology for calculating the calendar, ensuring consistency and uniformity across different regions and sects within the Islamic world. This promotes greater coherence and understanding regarding the timing of religious ceremonies.
Solar calendar compatibility:
The Hijri calendar, being based on lunar months, is shorter than the solar Gregorian calendar. Over time, this difference leads to a gradual deviation of Islamic histories compared to chapters. Astronomical calculations can facilitate the adjustment of the Hijri calendar to ensure its alignment with the solar year, reduce discrepancies and maintain the importance of Islamic dates in relation to agricultural rotations and seasonal events.
Merge leap days or months:
To address the discrepancy between lunar and solar years, astronomers can identify the need to include leap days or months in the Hijri calendar. By calculating the length of the lunar year and its deviation from the solar year, astronomers can recommend specific adjustments to maintain synchronization between the two calendars. This ensures the accuracy and stability of the Hijri calendar in the long run, which reduces the need for frequent revisions or adjustments.
Accessibility and technological integration:
Advances in astronomical science and technology have made astronomical calculations easier. Astronomical programs and online tools allow individuals, communities, and religious authorities to make accurate calculations and easily identify Islamic dates. This integration of technology facilitates the widespread adoption of astronomical methods for calculating the calendar, enhancing accuracy and reliability in determining Islamic dates and events.
Where is it used?

The Hijri calendar is mostly used in Muslim-majority areas, and spans across different countries in the Middle East, North Africa, Central Asia, and parts of Southeast Asia. Some countries and regions where the Hijri calendar is commonly used include:
Saudi Arabia:
As the cradle of Islam and home to the two holiest cities, Mecca and Medina, Saudi Arabia follows the Hijri calendar for all religious and official purposes. The country's government, religious institutions and authorities base their religious schedules, events, and ceremonies on the Hijri calendar. Islamic lunar months set important dates such as Ramadan.
Egypt:
As one of the most populous countries in the Arab world, Egypt follows the Hijri calendar alongside the Gregorian calendar. Islamic months and occasions such as Ramadan and Eid are widely celebrated, and the Hijri calendar is used for religious and cultural occasions.
Indonesian:
With the largest Muslim population in the world, Indonesia also follows the Hijri calendar for religious purposes. Although the country uses the Gregorian calendar primarily for official and administrative matters, Islamic holidays and religious rites are determined according to the Hijri calendar.
Pakistan:
As an Islamic Republic, Pakistan recognizes the Hijri calendar of religious and cultural events. Islamic months such as Ramadan and Muharram are of great importance, and the country celebrates Islamic holidays according to the lunar calendar.
Morocco:
In North Africa, Morocco follows the Hijri calendar for religious and cultural purposes. Islamic holidays are determined based on the lunar calendar, and the country's Muslim population fasts during the month of Ramadan according to Hijri dates.
Turkey:
While Turkey uses the Gregorian calendar primarily for official purposes, the Hijri calendar remains important for religious celebrations and Islamic holidays. The country's Muslim population follows the lunar calendar to determine the timing of Ramadan, Eid and other Islamic occasions.
These are just a few examples of countries where the Hijri calendar is widely used. However, it is important to note that the Islamic lunar calendar is followed by Muslims around the world, regardless of their geographical location, because it determines the timing of religious rites, festivals and celebrations in the Islamic faith.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using the Hijri year in daily life?

The use of the Hijri year in everyday life offers many pros and cons, which can vary depending on individual views and cultural contexts. Among them:
Positives:
Cultural and religious significance: The lunar calendar is deeply rooted in Islamic culture and history, making it an important aspect of Islamic identity, so that the crescent has become a symbol of Islam. Its use in daily life enhances the religious and cultural heritage of Islam, and fosters a sense of connection and belonging among Muslims around the world.
Compatibility with religious rites: The Hijri calendar facilitates the timing of religious rituals and events, including Ramadan, Eid al-Fitr, Eid al-Adha, and Hajj. Its lunar system ensures that these events occur continuously within the framework of Islamic months, allowing Muslims to plan and participate in religious activities accordingly.
Community cohesion: The widespread use of the Hijri calendar promotes unity and cohesion within Muslim societies. The joint celebration of Islamic dates and occasions also fosters a sense of solidarity and mutual understanding among Muslims around the world, strengthening social ties and collective identity.
Cyclical nature of time: The lunar cycle of the Hijri calendar reflects the cyclical nature of time in Islamic cosmology, focusing on the themes of renewal, meditation and spiritual growth. Their use encourages people to engage in periodic self-assessment, seek forgiveness, and set intentions for personal and spiritual development.
Negatives:
Incompatibility with the solar calendar: The Hijri calendar is based on lunar months, which results in a shorter year compared to the solar calendar. This discrepancy leads to an annual shift of Islamic dates relative to agricultural seasons and cycles, which can cause confusion and inconvenience in daily life.
Variation in moon visibility: The determination of Islamic months in the Hijri calendar depends on the sighting of the crescent, which can vary as mentioned above according to geographical location, weather conditions, and local practices of moon sighting. Discrepancies in moon visibility can lead to differences in the start dates of Islamic months between different Muslim communities, which can cause confusion and disagreements.
Interpolation challenges: To address the discrepancy between lunar and solar years, the Hijri calendar may require periodic adjustments by introducing leap days or months. However, determining the timing and necessity of interpolation can be complex and may vary between scientists and communities, which can lead to some disagreements.
Limited practical applications: While the Hijri calendar is widely used for religious and cultural purposes, its practical applications outside these contexts may be limited. In modern environments, where the Gregorian calendar is the standard for administrative, business and international purposes, the Hijri calendar may present challenges in daily scheduling, planning, and coordination. In general, the pros and cons of using the Hijri year in daily life reflect its profound importance in Islamic culture and its complexities in practice. Despite occasional contradictions or controversies, the Hijri calendar remains an integral part of Muslim life, as it is a symbol of the religious identity and spiritual heritage of Muslims around the world, guiding believers in their religious rites and cultural practices.
![]()
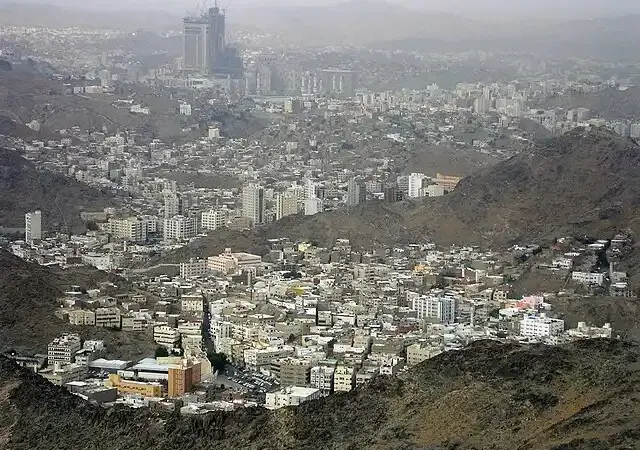
Makkah: A Journey of Faith to the Most Holy Place on Earth
Makkah is more than a city—it’s a powerful spiritual journey. Standing before the Kaaba, climbing Jabal al-Nur, or praying at Mount Arafat offers a deep connection to history, faith, and humanity. For any traveler, Mecca promises a unique and unforgettable experience rooted in timeless Islamic heritage. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
How to learn any language in a short time? 8 practical tips
There’s no quick fix for learning a language, but with steady effort and the right methods—like setting goals, practicing daily, or using apps like Duolingo—you’ll improve with time. Surround yourself with the language and focus on real-life use rather than just grammar. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
The importance of social communication for public health
The importance of social communication for public health more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
Traditional Syrian Glass Blowing : A Timeless Craft
Traditional Syrian Glass Blowing : A Timeless Craft more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
10 ways you can make money on YouTube
YouTube isn't just for watching videos anymore—it’s a legit way to make money. From joining the YouTube Partner Program to selling your own merch or offering paid memberships, there are plenty of smart ways to turn views into income and build a real career from your channel. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
At each moment, there are about 2,000 thunderstorms occurring on Earth.
Thunderstorms are powerful and common, with up to 2,000 happening worldwide at any time. Florida sees the most in the U.S., while Venezuela’s Lake Maracaibo holds the record for lightning. Remember: if you hear thunder, go inside—lightning can be deadly, even from miles away. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
The cave beneath Pembroke Castle and the fate of the early Britons
A hidden cave beneath Pembroke Castle has revealed ancient secrets, including animal fats and tools that trace the journey of early Britons from hunters to farmers. This incredible find brings new light to prehistoric life and the evolving habits of those who lived beneath the castle centuries before it was built. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
10 things smart people never share with anyone
Smart people often keep quiet about their true knowledge, finances, personal struggles, and future plans. It’s not secrecy—it’s strategy. By choosing what to share, they protect their peace, maintain control, and keep life’s noise at bay. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
A book that may interest you - Influence: The Psychology of Persuasion
A book that might interest you - Influence_ The Psychology of Persuasion more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
Extremely large telescopes: the next big thing in astronomy
Giant telescopes like the upcoming ELT and GMT are set to unlock deep cosmic secrets—from the first galaxies to possible signs of life on exoplanets. These powerful tools promise stunning discoveries and a clearer understanding of our universe’s origins and mysteries. more- ADVERTISEMENT