Reverse engineering of optimal beauty of evolution: revealing the scheme of nature
Nature has evolved over billions of years, refining and perfecting designs through trial and error. From the intricate patterns of butterfly wings to the streamlined body of the fish, evolution has created shapes that are not only functional but often aesthetically pleasing. As humans seek to solve complex problems and innovate in science and technology, there is a growing interest in reverse engineering the designs of the natural world – revealing nature's hidden wisdom and applying it to human challenges. This process allows to understand and replicate designs that have already stood the test of time, revealing the secrets behind the optimal beauty of evolution.
Show key points
- Reverse engineering involves breaking down objects or systems to understand their inner workings, originally applied to man-made technologies but increasingly relevant to natural designs.
- Nature offers a vast repository of efficient and elegant solutions evolved over billions of years, which scientists aim to replicate through reverse engineering.
- This process exposes both the functional benefits and the innate beauty of natural structures, such as the patterns in plants and the aerodynamic forms of birds.
- ADVERTISEMENT
- Reverse engineering nature can lead to breakthroughs in sustainability, healthcare, and design by mimicking traits like energy efficiency, regenerative ability, and structural integrity.
- Biomimicry builds on reverse engineering by applying biological insights directly into creating innovative human technologies, as seen in shark-skin-inspired antibacterial surfaces.
- With advancements in AI, 3D printing, and molecular biology, the future of reverse engineering promises enhanced replication and development of cutting-edge bio-inspired innovations.
- Ultimately, this practice fosters a harmonious blend of utility and aesthetics, helping humans design solutions that mirror nature’s time-tested efficiency and beauty.
In this article, we explore what reverse engineering is, how it applies to nature, the beauty in the process, and how humans can benefit from it. We'll also examine the relationship between reverse engineering in nature and biomime, and look to the future on how this concept of innovation is reshaping.
Recommend
1. Understand reverse engineering and its evolution.

Reverse engineering is the process of dismantling a system, object, or design to understand how it works, with the goal of replicating or improving it. Initially developed in the context of machinery, software and technology, reverse engineering involves dismantling a product to reveal its basic principles, designs and functions. By examining system components and how they work together, engineers can rebuild or improve the design, often discovering more efficient or innovative methods.
In technology, reverse engineering has led to breakthroughs in software development, product design, and manufacturing. But its potential extends far beyond artificial constructions. Nature, through billions of years of evolutionary fine-tuning, offers a vast landscape of mature designs for reverse engineering.
2. Reverse engineering in nature.
Nature's designs have been shaped by the pressures of survival and adaptation. Evolution, through natural selection, has improved these designs for optimal efficiency and flexibility, providing a great source of inspiration. When scientists and engineers reverse engineer biological structures and structures, they seek to understand the basic mechanisms of nature's solutions – how plants harness energy from sunlight, how animals regulate temperature, or how ecosystems balance themselves.
A notable example is the study of gecko feet. Through reverse engineering, scientists discovered that a gecko can cling to vertical surfaces due to microscopic hairs on its toes that create van der Waals forces. By replicating this natural design, engineers have developed advanced adhesives that can withstand significant weight and reusability. The development of such technologies demonstrates the enormous potential of reverse engineering in nature.
3. The beauty of reverse engineering in nature.
The reverse engineering process often reveals the beauty of complex systems designed in nature. Nature's designs are not only functional, but also have a stunning elegance. Let's consider the fractal patterns found in fern leaves or Fibonacci sequence in the arrangement of sunflower seeds – these mathematical patterns are visually pleasant and effective in using space.
Moreover, nature's solutions are sustainable and effective. For example, bird flight involves not only the mechanical efficiency of the wings, but also aerodynamic forms that reduce energy use. Reverse engineering in such natural wonders gives insight into how to harmoniously combine form and function, making nature's designs beautiful and effective.
4. How humans can benefit from the reverse engineering of nature.

The potential benefits of reverse engineering nature are enormous. By studying and replicating natural designs, humans can develop innovative technologies to solve contemporary problems. For example:
A. Sustainability: Nature's systems are inherently sustainable, working in harmony with the environment. Through reverse engineering processes such as photosynthesis or water filtration in plants, humans can create more sustainable technologies, such as energy-efficient solar panels or bio-inspired filtration systems.
B. Healthcare: The efficiency of living organisms offers breakthroughs in medical science. Learning how to regenerate the limbs of certain animals, or how to repair the natural systems of cells, can lead to advances in tissue regeneration, wound healing, and medical devices.
c. Architecture and Design: Nature's efficiency in structure and strength and flexibility are already being applied in architecture. For example, reverse engineering termite mounds has led to innovations in self-regulating ventilation systems in buildings, reducing energy consumption.
5.Reverse engineering in nature and biomimes.
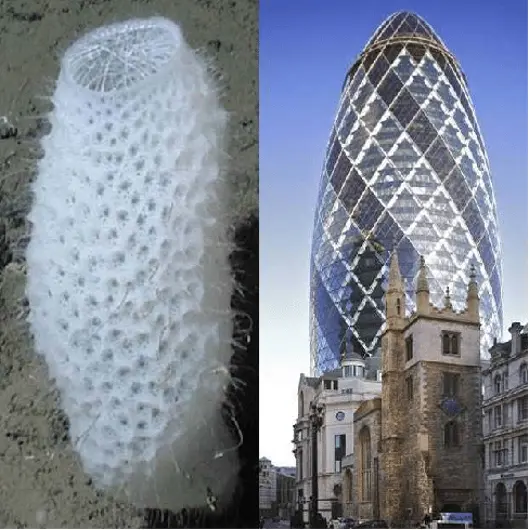

The term biomimetic refers to the practice of designing materials, structures, and systems that are modeled based on biological entities and processes. Biomimetic is closely related to reverse engineering in nature. While reverse engineering dissects and understands biological systems, biomimes apply this knowledge directly to the design of new products or technologies.
For example, studying the microstructure of shark skin led to the development of antibacterial surfaces in hospitals, which led to reduced infection rates. This is a clear case of reverse engineering that reveals how nature solves problems, followed by biomimes that apply this solution to human needs.
Reverse engineering often serves as the first step towards biomime, as understanding the complexities of natural systems provides the insights needed for imitation.
6. The future of reverse engineering in nature.
As technology continues to advance, the future of reverse engineering in nature promises exciting developments. Using tools such as three-dimensional printing, artificial intelligence and advanced computing, scientists will be able to model and replicate nature's designs more accurately. Furthermore, as a deeper understanding of genetic coding and molecular biology is gained, reverse engineering will extend from physical structures to the biological processes themselves, potentially leading to breakthroughs in bioengineering, synthetic biology, and regenerative medicine.
One of the most promising areas of reverse engineering in nature is the development of sustainable technologies. Nature designs are inherently efficient and waste-free, providing a blueprint for addressing the environmental challenges of the twenty-first century.
7. Reverse engineering for optimal beauty of evolution.

Evolution has created designs that are not only efficient, but also visually and structurally enhanced. The reverse engineering process of these designs allows humans to appreciate the cosmetic and functional beauty that nature has developed over thousands of years. By understanding the principles behind the bird's wing, spider web, or leaf structure, these shapes can be recreated to enhance existing technologies.
The optimal beauty of sophistication is reflected in its ability to balance efficiency, sustainability and aesthetics. Human creativity can benefit from this balance by reversing biological designs and introducing them into technology, architecture, and product development.
8. The future development of reverse engineering.
The future of reverse engineering will increasingly involve collaboration between biologists, engineers, architects, and computer scientists. As understanding of biological systems deepens, and as modeling and iteration tools evolve, reverse engineering will become the cornerstone of innovation.
We may soon reach a point where reverse engineering not only replicates nature's designs but creates entirely new solutions that exceed the efficiency and elegance of their natural counterparts.
The bottom line.

The optimal beauty of reverse engineering evolution is not only about understanding nature's solutions, but also about embracing the elegance and efficiency inherent in natural designs. By studying and replicating these systems, humans can benefit in areas such as sustainability, medicine, and technology. The interaction between reverse engineering and biomimes holds great promise for future innovations that are not only practical, but also in line with the natural world. As we move forward, the practice of reverse engineering the wisdom of nature will undoubtedly shape the course of human evolution, opening the door to practical solutions and a deeper appreciation of the beauty that nature has to offer.
![]()
Elon Musk - mad genius or unlimited diligence?
Elon Musk, dubbed the "Real Iron Man," is a bold, creative dreamer known for his ambition to colonize Mars, controversial tweets, and strict leadership style. Loved and hated, he's a complex figure who never shies away from challenges or attention, always pushing boundaries with fearless determination. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
Do you know why hair becomes white with age and not skin?
White hair can show up early due to genetics, stress, vitamin B12 deficiency, or smoking. While aging is a natural cause, lifestyle and health factors also play a role. Sometimes, treating underlying issues like thyroid problems or vitamin deficiencies may help restore hair color. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
Aswan City "Sono" ... Land of gold, tranquility and goodness
Aswan, once called Sono or the Land of Gold, is a magical city blending ancient history, stunning temples like Abu Simbel and Philae, and rare natural wonders—like shadowless solstice days. Its warm people, sun-filled skies, and legendary sites make it an unforgettable destination, especially in winter. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
Career path in the age of technology: strategies for choosing the right specialty
Technology is reshaping careers, making it vital to align personal passion with future trends. Choosing the right major now demands strategic planning, continuous learning, and adapting to rapid changes. Fields like AI, cybersecurity, and data science offer great promise for those ready to embrace innovation and flexibility. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
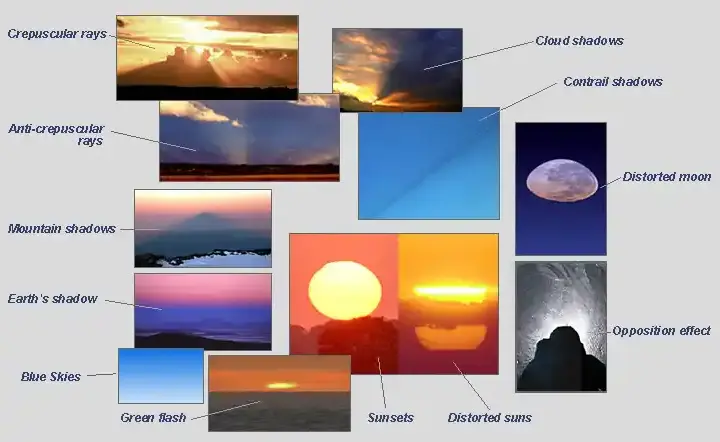
The most important unexplained heavenly phenomena that the world has witnessed
From glowing green flashes at sunset to fiery volcanic lightning and mysterious sky vortices, the heavens unveil rare phenomena that still baffle scientists. These atmospheric wonders continue to inspire awe as global research teams work to reveal their secrets through advanced observation and study. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
Simple ways to ascertain the nature of the curved ground
You don't need fancy tools or deep science to see Earth's curve—just use your camera, observe buildings, watch ships at sea, enjoy a flight, explore space photos, witness an eclipse, or study ocean tides. These simple experiences reveal the beautiful, curved nature of our planet in creative and exciting ways. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
We paint it wrong: the sun is not orange
The sun isn’t just orange—it’s a masterpiece of shifting colors. From pale reds and soft blues at dawn to radiant whites at noon, its beauty changes with time and weather. Films and culture fooled us, but nature tells a richer, truer story full of color and mystery. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
The dark side of early retirement
Early retirement sounds dreamy, but it's not all sunshine—many do it because they’re unhappy at work, feel hopeless, or want more time. But the risks are real: loneliness, regret, running out of money, and losing purpose. Think twice before jumping ship too early. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
Are electric cars actually making sales? Which countries are leading the way?
Electric vehicles are growing fast, with countries like Norway and China leading the way. Backed by government incentives and better tech, they offer lower costs and cleaner air. While challenges like high production costs remain, EVs are becoming a smart, eco-friendly choice for the future. more- ADVERTISEMENT
![]()
The Genius of Nature: 8 Amazing Technological Innovations Inspired by Nature
Nature inspires some of the coolest tech—like butterfly wings improving solar cells or kingfishers helping trains go quiet and fast. Even surgical needles got less painful thanks to mosquitoes. From firefly-inspired LEDs to Velcro born from prickly plants, the wild world is secretly shaping our everyday innovations. more- ADVERTISEMENT





















